Real-time PCR analysis of candidate imprinted genes on mouse chromosome 11 shows balanced expression from the maternal and paternal chromosomes and strain-specific variation in expression levels
- PMID: 18188004
- PMCID: PMC2507877
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.3.1.5469
Real-time PCR analysis of candidate imprinted genes on mouse chromosome 11 shows balanced expression from the maternal and paternal chromosomes and strain-specific variation in expression levels
Abstract
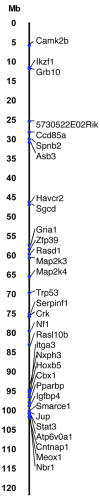
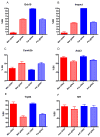
Imprinted genes are monoallelically expressed from either the maternal or paternal genome. Because cancer develops through genetic and epigenetic alterations, imprinted genes affect tumorigenesis depending on which parental allele undergoes alteration. We have shown previously in a mouse model of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) that inheriting mutant alleles of Nf1 and Trp53 on chromosome 11 from the mother or father dramatically changes the tumor spectrum of mutant progeny, likely due to alteration in an imprinted gene(s) linked to Nf1 and Trp53. In order to identify imprinted genes on chromosome 11 that are responsible for differences in susceptibility, we tested candidate imprinted genes predicted by a bioinformatics approach and an experimental approach. We have tested 30 candidate genes (Havcr2, Camk2b, Ccdc85a, Cntnap1, Ikzf1, 5730522E02Rik, Gria1, Zfp39, Sgcd, Jup, Nxph3, Spnb2, Asb3, Rasd1, Map2k3, Map2k4, Trp53, Serpinf1, Crk, Rasl10b, Itga3, Hoxb5, Cbx1, Pparbp, Igfbp4, Smarce1, Stat3, Atp6v0a1, Nbr1 and Meox1), two known imprinted genes (Grb10 and Impact) and Nf1, which has not been previously identified as an imprinted gene. Although we confirmed the imprinting of Grb10 and Impact, we found no other genes imprinted in the brain. We did, however, find strain-biased expression of Camk2b, 5730522E02Rik, Havcr2, Map2k3, Serpinf1, Rasl10b, Itga3, Asb3, Trp53, Nf1, Smarce1, Stat3, Cbx1, Pparbp and Cntnap1. These results suggest that the prediction of imprinted genes is complicated and must be individually validated. This manuscript includes supplementary data listing primer sequences for Taqman assays and Ct values for Taqman PCR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monoallelic loss of the imprinted gene Grb10 promotes tumor formation in irradiated Nf1+/- mice.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 22;11(5):e1005235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005235. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26000738 Free PMC article.
-
An imprinted locus epistatically influences Nstr1 and Nstr2 to control resistance to nerve sheath tumors in a neurofibromatosis type 1 mouse model.Cancer Res. 2006 Jan 1;66(1):62-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1480. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16397217 Free PMC article.
-
Thirteen genes (Cebpb, E2f1, Tcf4, Cyp24, Pck1, Acra4, Edn3, Kcnb1, Mc3r, Ntsr, Cd40, Plcg1 and Rcad) that probably lie in the distal imprinting region of mouse chromosome 2 are not monoallelically expressed.Genet Res. 1995 Apr;65(2):83-93. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300033103. Genet Res. 1995. PMID: 7781998
-
Imprinting of the mouse Igf2r gene depends on an intronic CpG island.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998 May 25;140(1-2):9-14. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(98)00022-7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9722161 Review.
-
Inducible uniparental chromosome disomy to probe genomic imprinting at single-cell level in brain and beyond.Neurochem Int. 2021 May;145:104986. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.104986. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Neurochem Int. 2021. PMID: 33600873 Review.
Cited by
-
Allelic expression of deleterious protein-coding variants across human tissues.PLoS Genet. 2014 May 1;10(5):e1004304. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004304. eCollection 2014 May. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24786518 Free PMC article.
-
Monoallelic loss of the imprinted gene Grb10 promotes tumor formation in irradiated Nf1+/- mice.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 22;11(5):e1005235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005235. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26000738 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretation of allele-specific chromatin accessibility using cell state-aware deep learning.Genome Res. 2021 Jun;31(6):1082-1096. doi: 10.1101/gr.260851.120. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Genome Res. 2021. PMID: 33832990 Free PMC article.
-
Serum biomarkers for neurofibromatosis type 1 and early detection of malignant peripheral nerve-sheath tumors.BMC Med. 2013 Apr 23;11:109. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-109. BMC Med. 2013. PMID: 23618374 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased expression of EFCC1 and its prognostic value in lung adenocarcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Nov;7(22):672. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.10.41. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31930073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feinberg AP, Tycko B. The history of cancer epigenetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:143–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
