Brief functional analysis and supplemental feeding for postmeal rumination in children with developmental disabilities
- PMID: 18189110
- PMCID: PMC2078561
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2007.743-747
Brief functional analysis and supplemental feeding for postmeal rumination in children with developmental disabilities
Abstract
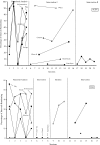
Rumination is a serious problem demonstrated by some people with developmental disabilities, but previous research has not included a functional analysis and has rarely compared intervention methods during the assessment process. We conducted functional analyses with 2 children who displayed postmeal rumination and subsequently evaluated a supplemental feeding intervention following meals. Results showed that noncontingent food or liquid presentation effectively reduced rumination with both children.
Figures
References
-
- Dudley L.L, Johnson C, Barnes S. Decreasing rumination using a starchy food satiation procedure. Behavioral Interventions. 2002;17:21–29.
-
- Heering P.W, Wilder D.A, Ladd C. Liquid rescheduling for the treatment of rumination. Behavioral Interventions. 2003;18:199–207.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical