Does intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) prevent additional toxicity of treating the pelvic lymph nodes compared to treatment of the prostate only?
- PMID: 18190681
- PMCID: PMC2253547
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-3-3
Does intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) prevent additional toxicity of treating the pelvic lymph nodes compared to treatment of the prostate only?
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the risk of rectal, bladder and small bowel toxicity in intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) of the prostate only compared to additional irradiation of the pelvic lymphatic region.
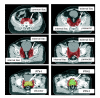
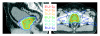
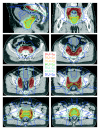
Methods: For ten patients with localized prostate cancer, IMRT plans with a simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) were generated for treatment of the prostate only (plan-PO) and for additional treatment of the pelvic lymph nodes (plan-WP). In plan-PO, doses of 60 Gy and 74 Gy (33 fractions) were prescribed to the seminal vesicles and to the prostate, respectively. Three plans-WP were generated with prescription doses of 46 Gy, 50.4 Gy and 54 Gy to the pelvic target volume; doses to the prostate and seminal vesicles were identical to plan-PO. The risk of rectal, bladder and small bowel toxicity was estimated based on NTCP calculations.
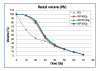
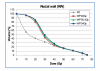
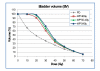
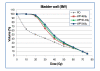
Results: Doses to the prostate were not significantly different between plan-PO and plan-WP and doses to the pelvic lymph nodes were as planned. Plan-WP resulted in increased doses to the rectum in the low-dose region </= 30 Gy, only, no difference was observed in the mid and high-dose region. Normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) for late rectal toxicity ranged between 5% and 8% with no significant difference between plan-PO and plan-WP. NTCP for late bladder toxicity was less than 1% for both plan-PO and plan-WP. The risk of small bowel toxicity was moderately increased for plan-WP.
Discussion: This retrospective planning study predicted similar risks of rectal, bladder and small bowel toxicity for IMRT treatment of the prostate only and for additional treatment of the pelvic lymph nodes.
Figures
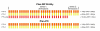
References
-
- Roach M, 3rd, DeSilvio M, Lawton C, Uhl V, Machtay M, Seider MJ, Rotman M, Jones C, Asbell SO, Valicenti RK, Han S, Thomas CR, Jr., Shipley WS. Phase III trial comparing whole-pelvic versus prostate-only radiotherapy and neoadjuvant versus adjuvant combined androgen suppression: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 9413. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1904–1911. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.05.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roach M, 3rd, Marquez C, Yuo HS, Narayan P, Coleman L, Nseyo UO, Navvab Z, Carroll PR. Predicting the risk of lymph node involvement using the pre-treatment prostate specific antigen and Gleason score in men with clinically localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994;28:33–37. - PubMed
-
- Lawton CA, Desilvio M, Roach M, 3rd, Uhl V, Kirsch R, Seider M, Rotman M, Jones C, Asbell S, Valicenti R, Hahn S, Thomas CR., Jr. An Update of the Phase III Trial Comparing Whole Pelvic to Prostate Only Radiotherapy and Neoadjuvant to Adjuvant Total Androgen Suppression: Updated Analysis of RTOG 94-13, with Emphasis on Unexpected Hormone/Radiation Interactions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69:646–655. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

