Phase II trial of cetuximab and carboplatin in relapsed platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer and evaluation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study
- PMID: 18191993
- PMCID: PMC2744339
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.11.029
Phase II trial of cetuximab and carboplatin in relapsed platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer and evaluation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study
Abstract
Purpose: This phase II trial assessed the activity and tolerability of cetuximab (C225, Erbitux) in combination with carboplatin in patients with relapsed platinum-sensitive ovarian or primary peritoneal carcinoma.
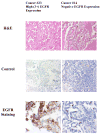
Patients and methods: Patients were to receive combination therapy with cetuximab (initial dose of 400 mg/m2 intravenously on cycle 1, day 1, followed by weekly infusions of 250 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC of 6 on day 1 and every 3 weeks). The primary objectives of this trial were to estimate the anti-tumor activity and adverse events of this combination therapy. Immunohistochemical expression of EGFR was evaluated in tumor specimens from patients enrolled in this trial.
Results: Of the 29 patients, 28 (97%) were eligible and evaluable for analysis of the efficacy and toxicity of cetuximab administered in combination with carboplatin. Of the evaluable entries, 26 had EGFR-positive tumors and the response rate in this group of patients was as follows: 9 demonstrated an objective response (3 CR; 6 PR) and 8 had stable disease. The response rate did not meet criteria for opening a second stage of accrual. The median time to progression was 9.4+ months (range: .9-22.2+). The most commonly observed adverse events were dermatologic toxicity (grade 3 in 32%), thrombocytopenia (grade 3 in 14%), and hypersensitivity reactions (grade 3 and 4 in 18%).
Conclusions: Cetuximab administered in combination with carboplatin had modest activity in screened patients with EGFR-positive, relapsed platinum-sensitive ovarian or primary peritoneal carcinoma. Cetuximab was associated with an acneiform rash in a majority of patients and occasional serious hypersensitivity reactions.
Figures
References
-
- Prewett M, Rockwell P, Rockwell RF, et al. The biologic effects of C225, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to the EGFR, on human prostate carcinoma. J Immunother. 1996;19:419–27. - PubMed
-
- Waksal HW. Role of an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor in treating cancer. Cancer & Metastasis Reviews. 1999;18:427–36. - PubMed
-
- Thompson DM, Gill GN. The EGF receptor: structure, regulation and potential role in malignancy. Cancer Surv. 1985;4:767–88. - PubMed
-
- Prewett M, Rothman M, Waksal H, Feldman M, Bander NH, Hicklin DJ. Mouse-human chimeric anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody C225 inhibits the growth of human renal cell carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res. 1998;4:2957–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous