Epigenetic regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 18192010
- PMCID: PMC4629448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2007.11.035
Epigenetic regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
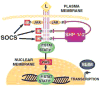
We have demonstrated that constitutive signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 activity, observed in approximately 50% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases, is associated with adverse treatment outcome. Constitutive STAT3 activation may result from the expression of oncogenic protein tyrosine kinases or from autocrine stimulation by hematopoietic growth factors. These causes are generally neither necessary nor sufficient for leukemogenesis; additional transforming events or growth stimulatory processes are needed. Here we review the literature addressing epigenetic regulation as a mechanism controlling STAT3 signaling in AML. A better understanding of mechanisms of dysregulation of STAT signaling pathways may serve as a basis for designing novel therapeutic strategies that target these pathways in leukemia cells.
Figures

References
-
- Xia Z, Baer MR, Block AW, Baumann H, Wetzler M. Expression of signal transducers and activators of transcription proteins in acute myeloid leukemia blasts. Cancer Res. 1998;58:3173–80. - PubMed
-
- Benekli M, Xia Z, Donohue KA, Ford LA, Pixley LA, Baer MR, et al. Constitutive activity of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 protein in acute myeloid leukemia blasts is associated with short disease-free survival. Blood. 2002;99:252–7. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard F, Tracy E, Smith J, Chattopadhyay S, Wang Y, et al. DNA methylation controls the responsiveness of hepatoma cells to leukemia inhibitory factor. Hepatology. 2003;38:1516–28. - PubMed
-
- Benekli M, Baer MR, Baumann H, Wetzler M. Signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins in leukemias. Blood. 2003;101:2940–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

