Apoptotic sphingolipid signaling by ceramides in lung endothelial cells
- PMID: 18192502
- PMCID: PMC2396244
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0274OC
Apoptotic sphingolipid signaling by ceramides in lung endothelial cells
Abstract
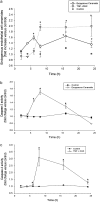
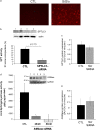
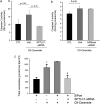
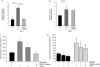
The de novo pathway of ceramide synthesis has been implicated in the pathogenesis of excessive lung apoptosis and murine emphysema. Intracellular and paracellular-generated ceramides may trigger apoptosis and propagate the death signals to neighboring cells, respectively. In this study we compared the sphingolipid signaling pathways triggered by the paracellular- versus intracellular-generated ceramides as they induce lung endothelial cell apoptosis, a process important in emphysema development. Intermediate-chain length (C(8:0)) extracellular ceramides, used as a surrogate of paracellular ceramides, triggered caspase-3 activation in primary mouse lung endothelial cells, similar to TNF-alpha-generated endogenous ceramides. Inhibitory siRNA against serine palmitoyl transferase subunit 1 but not acid sphingomyelinase inhibited both C(8:0) ceramide- and TNF-alpha (plus cycloheximide)-induced apoptosis, consistent with the requirement for activation of the de novo pathway of sphingolipid synthesis. Tandem mass spectrometry analysis detected increases in both relative and absolute levels of C(16:0) ceramide in response to C(8:0) and TNF-alpha treatments. These results implicate the de novo pathway of ceramide synthesis in the apoptotic effects of both paracellular ceramides and TNF-alpha-stimulated intracellular ceramides in primary lung endothelial cells. The serine palmitoyl synthase-regulated ceramides synthesis may contribute to the amplification of pulmonary vascular injury induced by excessive ceramides.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disruption of sphingolipid metabolism augments ceramide-induced autophagy in preeclampsia.Autophagy. 2015 Apr 3;11(4):653-69. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1034414. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25853898 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial fibroblasts and the sphingomyelinase pathway: sphingomyelin turnover and ceramide generation are not signaling mechanisms for the actions of tumor necrosis factor-alpha.Am J Pathol. 1998 Feb;152(2):505-12. Am J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9466577 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramide and apoptosis: exploring the enigmatic connections between sphingolipid metabolism and programmed cell death.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012 May;12(4):340-63. doi: 10.2174/187152012800228661. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 21707511 Review.
-
CFTR regulation of intracellular pH and ceramides is required for lung endothelial cell apoptosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Sep;41(3):314-23. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0264OC. Epub 2009 Jan 23. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19168702 Free PMC article.
-
[Sphingolipid-mediated apoptotic signaling pathways].J Soc Biol. 2003;197(3):217-21. J Soc Biol. 2003. PMID: 14708343 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Lung disease associated with alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010 Nov;7(6):381-6. doi: 10.1513/pats.201002-020AW. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010. PMID: 21030517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of lipid interactions on model vesicle engulfment by alveolar macrophages.Biophys J. 2014 Feb 4;106(3):598-609. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.12.036. Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 24507600 Free PMC article.
-
RTP801 is required for ceramide-induced cell-specific death in the murine lung.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Jan;48(1):87-93. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0254OC. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23024063 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic LPS inhalation causes emphysema-like changes in mouse lung that are associated with apoptosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Nov;39(5):584-90. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0448OC. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18539952 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids as cell fate regulators in lung development and disease.Apoptosis. 2015 May;20(5):740-57. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1112-6. Apoptosis. 2015. PMID: 25753687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kolesnick R, Fuks Z. Radiation and ceramide-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2003;22:5897–5906. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Shan P, Jiang D, Noble PW, Abraham NG, Kappas A, Lee PJ. Small interfering rna targeting heme oxygenase-1 enhances ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2004;279:10677–10684. - PubMed
-
- Slowik MR, De Luca LG, Min W, Pober JS. Ceramide is not a signal for tumor necrosis factor-induced gene expression but does cause programmed cell death in human vascular endothelial cells. Circ Res 1996;79:736–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

