Cardiovascular reactivity after blockade of angiotensin AT1 receptors in the experimental model of tilting test in conscious rats
- PMID: 18193073
- PMCID: PMC2267269
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707652
Cardiovascular reactivity after blockade of angiotensin AT1 receptors in the experimental model of tilting test in conscious rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Studies have shown that the angiotensin II AT(1) receptor antagonist, losartan, accentuates the hypotensive response in the orthostatic stress test (tilt) performed in anaesthetized rats. The same effect was not reported with other AT(1) antagonists. The aim of this study was to re-evaluate the effects of AT(1) receptor blockade on the cardiovascular response to tilt in a model developed for conscious rats.
Experimental approach: Rats (n=5-7 per group) were instrumented for infusion of drugs and recording of cardiovascular parameters and, after recovery, placed in a plastic tube positioned over the tilt board. The tilt test was conducted by raising the head side of the tilt board from horizontal position to 75 degrees head up position for 15 min.
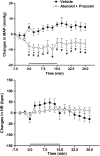
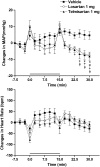
Key results: Compared with control group (NaCl 0.9%, 1 ml kg(-1)), oral treatment with 1 mg kg(-1) per day of losartan or telmisartan did not alter the blood pressure response during tilt. With the 10 mg kg(-1) dose, both antagonists altered the blood pressure response during tilt (mean maximum changes -11+/-3 mm Hg; P<0.01). A post-tilt hypotension was observed with both doses in losartan and telmisartan groups (-13+/-1 and -9+/-2 mm Hg, respectively; P<0.01).
Conclusions and implications: The present results indicate that the effect of losartan on the cardiovascular reactivity to tilt shares a similar profile to that of other AT(1) antagonists. Evidence discussed addresses the importance of using a conscious model for testing the influence of antihypertensive drugs on the cardiovascular reactivity to orthostatic challenges.
Figures



References
-
- Battershill AJ, Scott LJ. Telmisartan: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs. 2006;66:51–83. - PubMed
-
- Bedette D, Fontes MAP.Padronização de um método para avaliação das alterações cardiovasculares produzidas pela manobra de estresse ortostático em ratos acordados XIII Encontro de Pesquisa em Fisiologia e Farmacologia, MG, Brasil, Abstract 2005PGFisfar: Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil; 19vol. 1
-
- Colson P, Ryckwaert F, Coriat P. Renin angiotensin system antagonists and anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1999;89:1143–1155. - PubMed
-
- Dampney RA, Coleman MJ, Fontes MA, Hirooka Y, Horiuchi J, Li YW, et al. Central mechanisms underlying short- and long-term regulation of the cardiovascular system. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002;29:261–268. - PubMed
-
- Dampney RA, Horiuchi J, Tagawa T, Fontes MA, Potts PD, Polson JW. Medullary and supramedullary mechanisms regulating sympathetic vasomotor tone. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003;177:209–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

