Cytotoxic activity of polyacetylenes and polyenes isolated from roots of Echinacea pallida
- PMID: 18193076
- PMCID: PMC2267283
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707639
Cytotoxic activity of polyacetylenes and polyenes isolated from roots of Echinacea pallida
Abstract
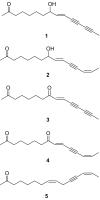
Background and purpose: The n-hexane extracts of the roots of three medicinally used Echinacea species exhibited cytotoxic activity on human cancer cell lines, with Echinacea pallida found to be the most cytotoxic. Acetylenes are present in E. pallida lipophilic extracts but essentially absent in extracts from the other two species. In the present study, the cytotoxic effects of five compounds, two polyacetylenes (namely, 8-hydroxy-pentadeca-(9E)-ene-11,13-diyn-2-one (1) and pentadeca-(9E)-ene-11,13-diyne-2,8-dione (3)) and three polyenes (namely, 8-hydroxy-pentadeca-(9E,13Z)-dien-11-yn-2-one (2), pentadeca-(9E,13Z)-dien-11-yne-2,8-dione (4) and pentadeca-(8Z,13Z)-dien-11-yn-2-one (5)), isolated from the n-hexane extract of E. pallida roots by bioassay-guided fractionation, were investigated and the potential bioavailability of these compounds in the extract was studied.
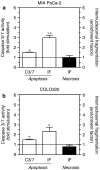
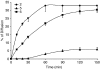
Experimental approach: Cytotoxic effects were assessed on human pancreatic MIA PaCa-2 and colonic COLO320 cancer cell lines. Cell viability was evaluated by the WST-1 assay and apoptotic cell death by the cytosolic internucleosomal DNA enrichment and the caspase 3/7 activity tests. Caco-2 cell monolayers were used to assess the potential bioavailability of the acetylenes.
Key results: The five compounds exhibited concentration-dependent cytotoxicity in both cell types, with a greater potency in the colonic cancer cells. Apoptotic cell death was found to be involved in the cytotoxic effect of the most active, compound 5. Compounds 2 and 5 were found to cross the Caco-2 monolayer with apparent permeabilities above 10 x 10(-6) cm s(-1).
Conclusions and implications: Compounds isolated from n-hexane extracts of E. pallida roots have a direct cytotoxicity on cancer cells and good potential for absorption in humans when taken orally.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation and structure elucidation of cytotoxic polyacetylenes and polyenes from Echinacea pallida.Phytochemistry. 2006 Jul;67(13):1359-64. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.05.006. Epub 2006 Jun 27. Phytochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16806329
-
A new method based on supercritical fluid extraction for polyacetylenes and polyenes from Echinacea pallida (Nutt.) Nutt. roots.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 Nov 30;146:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.07.053. Epub 2017 Aug 12. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017. PMID: 28841426
-
P-Glycoprotein inhibitory activity of lipophilic constituents of Echinacea pallida roots in a human proximal tubular cell line.Planta Med. 2008 Feb;74(3):264-6. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1034308. Planta Med. 2008. PMID: 18425719
-
High-performance liquid chromatography analysis of polyacetylenes and polyenes in Echinacea pallida by using a monolithic reversed-phase silica column.J Chromatogr A. 2007 May 11;1149(1):56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.11.038. Epub 2006 Nov 28. J Chromatogr A. 2007. PMID: 17126349
-
Analytical methods for the study of bioactive compounds from medicinally used Echinacea species.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Oct 25;160:443-477. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.07.044. Epub 2018 Aug 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 30142565 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Activities of Methanol, Ethanol and Supercritical CO2 Extracts of Philippine Piper betle L. on Clinical Isolates of Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria with Transferable Multiple Drug Resistance.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 7;11(1):e0146349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146349. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26741962 Free PMC article.
-
Echinacea sanguinea and Echinacea pallida extracts stimulate glucuronidation and basolateral transfer of Bauer alkamides 8 and 10 and ketone 24 and inhibit P-glycoprotein transporter in Caco-2 cells.Planta Med. 2013 Mar;79(3-4):266-74. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1328198. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Planta Med. 2013. PMID: 23408271 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous levels of Echinacea alkylamides and ketones are important contributors to the inhibition of prostaglandin E2 and nitric oxide production in cultured macrophages.J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Oct 14;57(19):8820-30. doi: 10.1021/jf901202y. J Agric Food Chem. 2009. PMID: 19807154 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol extract of Echinacea pallida reverses stress-delayed wound healing in mice.Phytomedicine. 2009 Jun;16(6-7):669-78. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2009.02.010. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Phytomedicine. 2009. PMID: 19303756 Free PMC article.
-
Enrichment of Echinacea angustifolia with Bauer alkylamide 11 and Bauer ketone 23 increased anti-inflammatory potential through interference with cox-2 enzyme activity.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Aug 11;58(15):8573-84. doi: 10.1021/jf1014268. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20681645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artursson P, Karlsson J. Correlation between oral drug absorption in humans and apparent drug permeability coefficients in human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;175:880–885. - PubMed
-
- Bador P, Paris J. Acetylenic enzyme inhibitors: their role in anticancer chemotherapy. Pharm Acta Helv. 1990;65:305–310. - PubMed
-
- Barnes J, Anderson LA, Gibbons S, Phillipson JD. Echinacea species (Echinacea angustifolia (DC.) Hell., Echinacea pallida (Nutt.) Nutt., Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench): a review of their chemistry, pharmacology and clinical properties. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005;57:929–954. - PubMed
-
- Bauer R, Khan IA, Wagner H. TLC and HPLC analysis of Echinacea pallida and Echinacea angustifolia roots. Planta Med. 1988a;54:426–430. - PubMed
-
- Bauer R, Remiger P. TLC and HPLC analysis of alkamides in Echinacea drugs1, 2. Planta Med. 1989;55:367–371. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

