Lansoprazole-induced improvement of esophageal submucosal injury
- PMID: 18193102
- PMCID: PMC2170952
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.2007013
Lansoprazole-induced improvement of esophageal submucosal injury
Abstract
The proton pumpvinhibitor, lansoprazole, is reported to have acid secretion inhibiting effect as well as anti-inflammatory effects such as inhibition of cytokine secretion from inflammatory cells. Clinically, excellent efficacy of lansoprazole is reported for not only gastric ulcer but also gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Since GERD is categorized endoscopically into erosive esophagitis and non-erosive reflux disease, it is important to make accurate assessment of any improvement in the inflammatory process when using endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) capable of visualizing the submucosal structure. We report here our experience in assessing the effect of treatment with lansoprazole on esophageal wall structure using EUS in patients with GERD. At baseline (before treatment), EUS showed abnormalities in the mucosa, submucosa and muscularis propria caused by inflammation, thickening of the entire esophageal wall and changes in the contractile properties of esophageal smooth muscles reflecting the effects of inflammation on the entire wall of the lower esophagus in reflux esophagitis regardless of whether it is erosive or endoscopically-negative. Treatment with lansoprazole resulted in normalization of esophageal wall structure and improvement of motility, suggesting that lansoprazole improves not only mucosal inflammation but also submucosal inflammation in GERD.
Keywords: GERD; endoscopic ultrasonography; esophageal wall structure; lansoprazole.
Figures
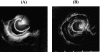
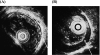
Similar articles
-
Ultrasonographic evaluation of lansoprazole-induced improvement of submucosal injury in patients with gastroesophageal reflux.Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Feb;95(2):381-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.01757.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000. PMID: 10685739 Clinical Trial.
-
Increased esophageal mucosal/submucosal blood flow in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: normalization by treatment with a proton pump inhibitor.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Feb;23(2):303-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05113.x. Epub 2007 Aug 27. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 17725600 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the effect of lansoprazole and omeprazole on intragastric acidity and gastroesophageal reflux in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease.Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998 Dec;33(12):1239-43. doi: 10.1080/00365529850172304. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998. PMID: 9930385 Clinical Trial.
-
Drugs, bugs, and esophageal pH profiles.Yale J Biol Med. 1999 Mar-Jun;72(2-3):169-72. Yale J Biol Med. 1999. PMID: 10780578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2006 Nov;82(5 Suppl):S133-45. doi: 10.2223/JPED.1555. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2006. PMID: 17136289 Review.
Cited by
-
Brief Questioning by Nursing Staffs before Endoscopic Examination May Not Always Pick Up Clinical Symptoms of Endoscopic Reflux Esophagitis.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010 May;46(3):229-33. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.09-96. Epub 2010 Apr 10. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20490318 Free PMC article.
-
Proton pump inhibitors and gastritis.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2008 Mar;42(2):71-5. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.2008012. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18385822 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of NSAID-Induced Small Intestinal Mucosal Injury: Prophylactic Potential of Lansoprazole.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2009 Sep;45(2):125-30. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.SR09-58. Epub 2009 Aug 28. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19794918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vakil N., van Zaten S.V., Kahrilas P., Dent J., Jones R. the Global Consensus Group: The montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1900–1920. - PubMed
-
- Havelund T., Lind T., Wiklund I., Glise H., Hernqvist H., Lauritsen K., Lundell L., Pedersen S.A., Carlson R., Junghard O., Stubberod A., Anker-Hansen O. Quality of life in patients with heartburn but without esophagitis: effects of treatment with omeprazole. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999;94:1782–1789. - PubMed
-
- Lagergren J., Bergstrom R., Lindgren A., Nyren O. Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux as a risk factor for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;340:825–831. - PubMed
-
- Locke G.R., Tally N.J., Fett S.L., Zinsmeister A.R., Melton L.J. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: a population-based study in Olmsted Country, Minnesota. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:1448–1456. - PubMed
-
- Orland R.C. Reflux esophagitis. In: Yamada T., Alpers D.H., Owyang C., Powell D.W., Laine L., editors. in Textbook of gastroenterology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 1999. pp. 1235–1263.

