Geranylgeranylacetone ameliorates inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in murine macrophages: inhibition of LPS binding to the cell surface
- PMID: 18193105
- PMCID: PMC2170953
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.2007016
Geranylgeranylacetone ameliorates inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in murine macrophages: inhibition of LPS binding to the cell surface
Abstract
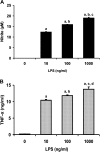
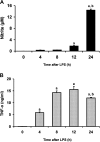
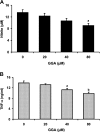
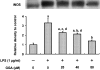
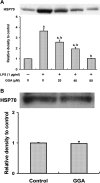
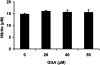
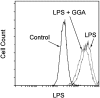
We investigated whether pretreatment with geranylgeranylacetone (GGA), a potent heat shock protein (HSP) inducer, could inhibit proinflammatory cytokine liberation and nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated murine macrophages. The levels of NO and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) released from murine macrophage RAW 264 cells were increased dose- and time-dependently following treatment with LPS (1 microg/ml). GGA (80 microM) treatment 2 h before LPS addition significantly suppressed TNF-alpha and NO productions at 12 h and 24 h after LPS, respectively, indicating that GGA inhibits activation of macrophages. However, replacement by fresh culture medium before LPS treatment abolished the inhibitory effect of GGA on NO production in LPS-treated cells. Furthermore, GGA inhibited both HSP70 and inducible NO synthase expressions induced by LPS treatment despite an HSP inducer. When it was examined whether GGA interacts with LPS and/or affects expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and CD14 on the cell surface, GGA inhibited the binding of LPS to the cell surface, while GGA did not affect TLR4 and CD14 expressions. These results indicate that GGA suppresses the binding of LPS to the cell surface of macrophages, resulting in inhibiting signal transduction downstream of TLR4.
Keywords: Geranylgeranylacetone; lipopolysaccharide; macrophage; nitric oxide; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oral administration of geranylgeranylacetone improves survival rate in a rat endotoxin shock model: administration timing and heat shock protein 70 induction.Shock. 2005 Nov;24(5):482-7. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000180980.63247.a9. Shock. 2005. PMID: 16247336
-
Ketamine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 gene expressions in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages through suppression of toll-like receptor 4-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation and activator protein-1 activation.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 1;228(1):105-13. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.11.027. Epub 2007 Dec 8. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18191973
-
An anti-ulcer drug, geranylgeranylacetone, suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells.J Hypertens. 2005 Oct;23(10):1847-53. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000182525.74934.c0. J Hypertens. 2005. PMID: 16148608
-
Inhibitory effect of naringin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxin shock in mice and nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Life Sci. 2006 Jan 11;78(7):673-81. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.04.051. Epub 2005 Aug 31. Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16137700
-
Ginsenoside Re ameliorates inflammation by inhibiting the binding of lipopolysaccharide to TLR4 on macrophages.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Sep 26;60(38):9595-602. doi: 10.1021/jf301372g. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22849695
Cited by
-
Zinc Supplementation with Polaprezinc Protects Mouse Hepatocytes against Acetaminophen-Induced Toxicity via Induction of Heat Shock Protein 70.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010 Jan;46(1):43-51. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.09-60. Epub 2009 Dec 29. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20104264 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of geranylgeranylacetone via enhancement of HSPB8 induction in desmin-related cardiomyopathy.PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005351. Epub 2009 Apr 28. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19399179 Free PMC article.
-
Polaprezinc Protects Mice against Endotoxin Shock.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010 May;46(3):234-43. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.09-125. Epub 2010 Apr 10. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20490319 Free PMC article.
-
Redox Potential-Sensitive N-Acetyl Cysteine-Prodrug Nanoparticles Inhibit the Activation of Microglia and Improve Neuronal Survival.Mol Pharm. 2017 May 1;14(5):1591-1600. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b01028. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Mol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28335600 Free PMC article.
-
Geranylgeranylacetone Ameliorates Skin Inflammation by Regulating and Inducing Thioredoxin via the Thioredoxin Redox System.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 31;12(9):1701. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091701. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S. Mammalian Toll-like receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003;15:5–11. - PubMed
-
- Klosterhalfen B., Hauptmann S., Offner F.A., Amo-Takyi B., Tons C., Winkeltau G., Affify M., Kupper W., Kirkpatrick C.J., Mittermayer C. Induction of heat shock protein 70 by zinc-bis-(DL-hydrogenaspartate) reduces cytokine liberation, apoptosis, and mortality rate in a rat model of LD100 endotoxiemia. Shock. 1997;7:254–262. - PubMed
-
- Carrillo-Vico A., Lardone P.J., Naji L., Fernández-Santos J.M., Martín-Lacave I., Guerrero J.M., Calvo J.R. Beneficial pleiotropic actions of melatonin in an experimental model of septic shock in mice: regulation of pro-/anti-inflammatory cytokine network, protection against oxidative damage and anti-apoptotic effects. J. Pineal Res. 2005;39:400–408. - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama T., Fujita M., Koide N., Mori I., Yoshida T., Mori H., Yokochi T. 2-Aminopurine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production by preventing IFN-β production. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004;48:957–963. - PubMed
-
- Jantaratnotai N., Utaisincharoen P., Piyachaturawat P., Chongthammakun S., Sanvarinda Y. Inhibitory effect of Curcuma comosa on NO production and cytokine expression in LPS-activated microglia. Life Sci. 2006;78:571–577. - PubMed

