The spectrum of diabetic neuropathies
- PMID: 18194747
- PMCID: PMC2720624
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pmr.2007.10.010
The spectrum of diabetic neuropathies
Abstract
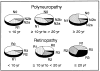
Diabetes mellitus is associated with many different neuropathic syndromes, ranging from a mild sensory disturbance as can be seen in a diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy, to the debilitating pain and weakness of a diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy. The etiology of these syndromes has been studied extensively, and may vary among metabolic, compressive, and immunological bases for the different disorders, as well as mechanisms yet to be discovered. Many of these disorders of nerve appear to be separate conditions with different underlying mechanisms, and some are caused directly by diabetes mellitus, whereas others are associated with it but not caused by hyperglycemia. This article discusses a number of the more common disorders of nerve found with diabetes mellitus. It discusses the symmetrical neuropathies, particularly generalized diabetic polyneuropathy, and then the focal or asymmetrical types of diabetes-associated neuropathy.
Figures


References
-
- Leyden E. Beitrag zur Klinik des diabetes mellitus. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1893;43:926.
-
- Dyck PJB, Dyck PJ. Paresthesia, pain and weakness in hands of diabetic patients is attributable to mononeuropathies or radiculopathy, not polyneuropathy: The Rochester (RDNS) and Pancreas Renal Transplant (MC-PRT) Studies. Neurology. 1998;50:A333.
-
- Tracy JA, Dyck PJB, Harper CM, et al. Hand symptomatology in diabetes usually due to mononeuropathy, not polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol. 2005;58(Suppl 9):S36.
-
- Dyck PJ, O’Brien PC, Litchy WJ, et al. Monotonicity of nerve tests in diabetes. Subclinical nerve dysfunction precedes diagnosis of polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(9):2192–200. - PubMed
-
- Gregersen G. Diabetic neuropathy: Influence of age, sex metabolic control, and duration of diabetes on motor conduction velocity. Neurology. 1967;17:972–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

