Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin acts as an alarmin to activate the TLR2-MyD88 signal pathway in dendritic cells and enhances Th2 immune responses
- PMID: 18195069
- PMCID: PMC2234357
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20062027
Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin acts as an alarmin to activate the TLR2-MyD88 signal pathway in dendritic cells and enhances Th2 immune responses
Abstract
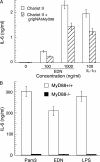
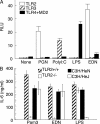
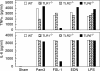
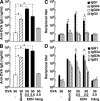
Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) is an eosinophil granule-derived secretory protein with ribonuclease and antiviral activity. We have previously shown that EDN can induce the migration and maturation of dendritic cells (DCs). Here, we report that EDN can activate myeloid DCs by triggering the Toll-like receptor (TLR)2-myeloid differentiation factor 88 signaling pathway, thus establishing EDN as an endogenous ligand of TLR2. EDN activates TLR2 independently of TLR1 or TLR6. When mice were immunized with ovalbumin (OVA) together with EDN or with EDN-treated OVA-loaded DCs, EDN enhanced OVA-specific T helper (Th)2-biased immune responses as indicated by predominant production of OVA-specific interleukin (IL)-5, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-13, as well as higher levels of immunoglobulin (Ig)G1 than IgG2a. Based on its ability to serve as a chemoattractant and activator of DCs, as well as the capacity to enhance antigen-specific immune responses, we consider EDN to have the properties of an endogenous alarmin that alerts the adaptive immune system for preferential enhancement of antigen-specific Th2 immune responses.
Figures



Comment in
-
Alarming dendritic cells for Th2 induction.J Exp Med. 2008 Jan 21;205(1):13-7. doi: 10.1084/jem.20072665. Epub 2008 Jan 14. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 18195077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zasloff, M. 2002. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature. 415:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Ganz, T. 2003. Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:710–720. - PubMed
-
- Yang, D., A. Biragyn, D.M. Hoover, J. Lubkowski, and J.J. Oppenheim. 2004. Multiple roles of antimicrobial defensins, cathelicidins, and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in host defense. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22:181–315. - PubMed
-
- Yang, D., and J.J. Oppenheim. 2004. Antimicrobial proteins act as “alarmins” in joint immune defense. Arthritis Rheum. 50:3401–3403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

