Towards a pathway definition of Parkinson's disease: a complex disorder with links to cancer, diabetes and inflammation
- PMID: 18196299
- PMCID: PMC2238789
- DOI: 10.1007/s10048-007-0116-y
Towards a pathway definition of Parkinson's disease: a complex disorder with links to cancer, diabetes and inflammation
Abstract
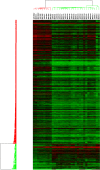
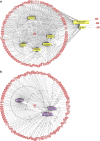
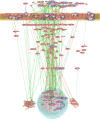
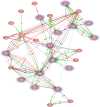
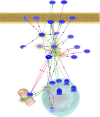
We have previously established a first whole genome transcriptomic profile of sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD). After extensive brain tissue-based validation combined with cycles of iterative data analysis and by focusing on the most comparable cases of the cohort, we have refined our analysis and established a list of 892 highly dysregulated priority genes that are considered to form the core of the diseased Parkinsonian metabolic network. The substantia nigra pathways, now under scrutiny, contain more than 100 genes whose association with PD is known from the literature. Of those, more than 40 genes belong to the highly significantly dysregulated group identified in our dataset. Apart from the complete list of 892 priority genes, we present pathways revealing PD 'hub' as well as 'peripheral' network genes. The latter include Lewy body components or interact with known PD genes. Biological associations of PD with cancer, diabetes and inflammation are discussed and interactions of the priority genes with several drugs are provided. Our study illustrates the value of rigorous clinico-pathological correlation when analysing high-throughput data to make optimal use of the histopathological phenome, or morphonome which currently serves as the key diagnostic reference for most human diseases. The need for systematic human tissue banking, following the highest possible professional and ethical standard to enable sustainability, becomes evident.
Figures
References
-
- Tretiakoff C (1919) Contribution à l’étude de l’anatomie du locus niger de Soemmering avec quelques déductions relatives à la pathogenie des troubles du tonus musculaire et de la maladie de Parkinson. Thèse de Paris
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1126/science.276.5321.2045', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5321.2045'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9197268', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9197268/'}]}
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/s10048-005-0020-2', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-005-0020-2'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16344956', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16344956/'}]}
- Moran LB, Duke DC, Deprez M, Dexter DT, Pearce RK, Graeber MB (2006) Whole genome expression profiling of the medial and lateral substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Neurogenetics 7:1–11 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1001/archneur.62.6.917', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.62.6.917'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15956162', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15956162/'}]}
- Hauser MA, Li YJ, Xu H, Noureddine MA, Shao YS, Gullans SR, Scherzer CR, Jensen RV, McLaurin AC, Gibson JR, Scott BL, Jewett RM, Stenger JE, Schmechel DE, Hulette CM, Vance JM (2005) Expression profiling of substantia nigra in Parkinson disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, and frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism. Arch Neurol 62:917–921 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15965975', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15965975/'}]}
- Zhang Y, James M, Middleton FA, Davis RL (2005) Transcriptional analysis of multiple brain regions in Parkinson’s disease supports the involvement of specific protein processing, energy metabolism, and signaling pathways, and suggests novel disease mechanisms. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 137:5–16 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

