Dioxin exposure, from infancy through puberty, produces endocrine disruption and affects human semen quality
- PMID: 18197302
- PMCID: PMC2199303
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.10399
Dioxin exposure, from infancy through puberty, produces endocrine disruption and affects human semen quality
Abstract
Background: Environmental toxicants are allegedly involved in decreasing semen quality in recent decades; however, definitive proof is not yet available. In 1976 an accident exposed residents in Seveso, Italy, to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD).
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate reproductive hormones and sperm quality in exposed males.
Methods: We studied 135 males exposed to TCDD at three age groups, infancy/prepuberty (1-9 years), puberty (10-17 years), and adulthood (18-26 years), and 184 healthy male comparisons using 1976 serum TCDD levels and semen quality and reproductive hormones from samples collected 22 years later.
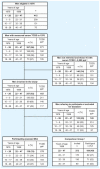
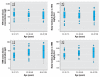
Results: Relative to comparisons, 71 men (mean age at exposure, 6.2 years; median serum TCDD, 210 ppt) at 22-31 years of age showed reductions in sperm concentration (53.6 vs. 72.5 million/mL; p = 0.025); percent progressive motility (33.2% vs. 40.8%; p < 0.001); total motile sperm count (44.2 vs. 77.5 x 10(6); p = 0.018); estradiol (76.2 vs. 95.9 pmol/L; p = 0.001); and an increase in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH; 3.58 vs. 2.98 IU/L; p = 0.055). Forty-four men (mean age at exposure, 13.2 years; median serum TCDD, 164 ppt) at 32-39 years of age showed increased total sperm count (272 vs. 191.9 x 10(6); p = 0.042), total motile sperm count (105 vs. 64.9 x10(6); p = 0.036), FSH (4.1 vs. 3.2 UI/L; p = 0.038), and reduced estradiol (74.4 vs. 92.9 pmol/L; p < 0.001). No effects were observed in 20 men, 40-47 years of age, who were exposed to TCDD (median, 123 ppt) as adults (mean age at exposure, 21.5 years).
Conclusions: Exposure to TCDD in infancy reduces sperm concentration and motility, and an opposite effect is seen with exposure during puberty. Exposure in either period leads to permanent reduction of estradiol and increased FSH. These effects are permanent and occur at TCDD concentrations < 68 ppt, which is within one order of magnitude of those in the industrialized world in the 1970s and 1980s and may be responsible at least in part for the reported decrease in sperm quality, especially in younger men.
Keywords: TCDD; dioxin; endocrine disruption; environmental contaminants; human sperm quality; reproductive hormones.
Figures

References
-
- Andersen AG, Jensen TK, Carlsen E, Jorgensen N, Andersson AM, Krarup T. High frequency of sub-optimal semen quality in an unselected population of young men. Hum Reprod. 2000;15:366–372. - PubMed
-
- Atanassova NN, Walker M, McKinnell C, Fisher JS, Sharpe RM. Evidence that androgens and oestrogens, as well as follicle-stimulating hormone, can alter Sertoli cell number in the neonatal rat. J Endocrinol. 2005;184:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Auger J, Kunstmann JM, Czyglik F, Jouannet P. Decline in semen quality among fertile men in Paris during the past 20 years. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:281–285. - PubMed
-
- Aylward LL, Brunet RC, Carrier G, Hays SM, Cushing CA, Needham LL, et al. Concentration-dependent TCDD elimination kinetics in humans: toxicokinetic modelling for moderately to highly exposed adults from Seveso, Italy, and Vienna, Austria, and impact on dose estimates for the NIOSH cohort. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol. 2005;15:51–65. - PubMed

