Regulation of aicda expression and AID activity: relevance to somatic hypermutation and class switch DNA recombination
- PMID: 18197815
- PMCID: PMC2994649
- DOI: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v27.i4.60
Regulation of aicda expression and AID activity: relevance to somatic hypermutation and class switch DNA recombination
Abstract
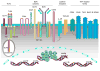
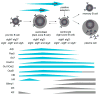
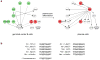
Expression and activity of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) encoded by the aicda gene are essential for immunoglobulin (Ig) gene somatic hypermutation (SHM) and class switch DNA recombination (CSR). SHM and CSR unfold, in general, in germinal centers and/are central to the maturation of effective antibody responses. AID expression is induced by activated B-cell CD40 signaling, which is critical for the germinal center reaction, and is further enhanced by other stimuli, including interleukin-4 (IL-4) secreted from CD4+ T cells or Toll-like receptor (TLR)-activating bacterial and/or viral molecules. Integration of different intracellular signal transduction pathways, as activated by these stimuli, leads to a dynamic aicda-regulating program, which involves both positively acting trans-factors, such as Pax5, HoxC4, E47, and Irf8, and negative modulators, such as Blimp1 and Id2, to restrict aicda expression primarily to germinal center B cells. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-K), which functions downstream of activated B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, likely plays an important role in triggering the downregulation of aicda expression in postgerminal center B cells and throughout plasmacytoid differentiation. In B cells undergoing SHM and CSR, AID activity, and, possibly, AID targeting to the Ig locus are regulated at a posttranslational level, including AID dimerization/oligomerization, nuclear/cytoplasmic AID translocation, and phosphorylation of the AID Ser38 residue by protein kinase A (PKA). Here, we discuss the role of B-cell activation signals, transcription regulation programs, and posttranslational modifications in controlling aicda expression and AID activity, thereby delineating an integrated model of modulation of SHM and CSR in the germinal center reaction.
Figures
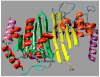

Similar articles
-
HoxC4 binds to the promoter of the cytidine deaminase AID gene to induce AID expression, class-switch DNA recombination and somatic hypermutation.Nat Immunol. 2009 May;10(5):540-50. doi: 10.1038/ni.1725. Epub 2009 Apr 12. Nat Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19363484 Free PMC article.
-
A Hyper-IgM Syndrome Mutation in Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase Disrupts G-Quadruplex Binding and Genome-wide Chromatin Localization.Immunity. 2020 Nov 17;53(5):952-970.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.10.003. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 33098766 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Heterozygous Variant in AICDA Impairs Ig Class Switching and Somatic Hypermutation in Human B Cells and is Associated with Autosomal Dominant HIGM2 Syndrome.J Clin Immunol. 2024 Feb 16;44(3):66. doi: 10.1007/s10875-024-01665-1. J Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38363477 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Aicda expression and AID activity.Autoimmunity. 2013 Mar;46(2):83-101. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2012.749244. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Autoimmunity. 2013. PMID: 23181381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex regulation and function of activation-induced cytidine deaminase.Trends Immunol. 2011 May;32(5):194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.03.003. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Trends Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21493144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase and aberrant germinal center selection in the development of humoral autoimmunities.Am J Pathol. 2011 Feb;178(2):462-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.09.044. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21281778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) linking immunity, chronic inflammation, and cancer.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012 Sep;61(9):1591-8. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1255-z. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012. PMID: 22527246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonamer dependent RAG cleavage at CpGs can explain mechanism of chromosomal translocations associated to lymphoid cancers.PLoS Genet. 2022 Oct 13;18(10):e1010421. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010421. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36228010 Free PMC article.
-
Paradoxical role of Id proteins in regulating tumorigenic potential of lymphoid cells.Front Med. 2018 Aug;12(4):374-386. doi: 10.1007/s11684-018-0652-x. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Front Med. 2018. PMID: 30043222 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Reactivation Induces IgG4 Production by Host B Lymphocytes in Graves' Disease Patients and Controls: A Subset of Graves' Disease Is an IgG4-Related Disease-Like Condition.Viral Immunol. 2018 Oct;31(8):540-547. doi: 10.1089/vim.2018.0042. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Viral Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30222515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin A, Scharff MD. AID and mismatch repair in antibody diversification. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:605–14. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri J, Alt FW. Class-switch recombination: interplay of transcription, DNA deamination and DNA repair. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:541–52. - PubMed
-
- Maizels N. Immunoglobulin gene diversification. Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:23–46. - PubMed
-
- Odegard VH, Schatz DG. Targeting of somatic hypermutation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:573–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

