GPCR monomers and oligomers: it takes all kinds
- PMID: 18199492
- PMCID: PMC2366802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2007.11.007
GPCR monomers and oligomers: it takes all kinds
Abstract
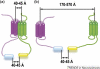
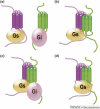
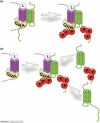
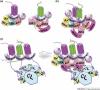
Accumulating evidence of G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) oligomerization on the one hand and perfect functionality of monomeric receptors on the other creates an impression of controversy. However, the GPCR superfamily is extremely diverse, both structurally and functionally. The life cycle of each receptor includes many stages: synthesis, quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum, maturation in the Golgi, delivery to the plasma membrane (where it can be in the inactive or active state, in complex with cognate G protein, G-protein-coupled receptor kinase or arrestin), endocytosis and subsequent sorting in endosomes. Different GPCR subtypes, and even the same receptor at different stages of its life cycle, most likely exist in different oligomerization states, from monomers to dimers and possibly higher-order oligomers.
Figures
References
-
- Moore CA, et al. Regulation of receptor trafficking by GRKs and arrestins. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007;69:451–482. - PubMed
-
- Gurevich VV, Gurevich EV. The molecular acrobatics of arrestin activation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004;25:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Goodman OB,, Jr, et al. β-Arrestin acts as a clathrin adaptor in endocytosis of the β2-adrenergic receptor. Nature. 1996;383:447–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

