Does arginine remain protonated in the lipid membrane? Insights from microscopic pKa calculations
- PMID: 18199662
- PMCID: PMC2275699
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.122945
Does arginine remain protonated in the lipid membrane? Insights from microscopic pKa calculations
Abstract
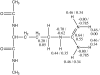
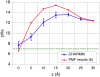
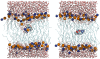
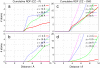
Free energy perturbation calculations are carried out to estimate the effective pK(a) of an arginine (Arg) sidechain as a function of its location in the dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer. Similar to previous all-atom simulations of the voltage sensor domain of a potassium channel in the membrane with charged Arg residues, the membrane and water structures deform to stabilize the charge of the Arg analog. As a result, the computed pK(a) is >7 throughout the membrane although the value is very close to 7 near the center of the bilayer. With additional stabilizations from negatively charged amino acids or lipid molecules, it is reasonable to expect that Arg in membrane proteins (once in the membrane) can adopt the protonated state despite the low dielectric nature of the bulk lipid membrane.
Figures
References
-
- Jiang, Y., A. Lee, J. Chen, V. Ruta, M. Cadene, B. T. Chait, and R. MacKinnon. 2003. X-ray structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature. 423:33–41. - PubMed
-
- Hessa, T., H. Kim, K. Bihlmaier, C. Lundin, J. Boekel, H. Andersson, I. Nilsson, S. H. White, and G. von Heijne. 2005. Recognition of transmembrane helices by the endoplasmic reticulum translocon. Nature. 433:377–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

