Changes in the hyperelastic properties of endothelial cells induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- PMID: 18199670
- PMCID: PMC2275697
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.106.099333
Changes in the hyperelastic properties of endothelial cells induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha
Abstract
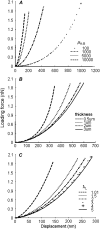
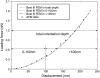
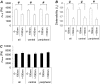
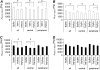
Mechanical properties of living cells can be determined using atomic force microscopy (AFM). In this study, a novel analysis was developed to determine the mechanical properties of adherent monolayers of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (ECs) using AFM and finite element modeling, which considers both the finite thickness of ECs and their nonlinear elastic properties, as well as the large strain induced by AFM. Comparison of this model with the more traditional Hertzian model, which assumes linear elastic behavior, small strains, and infinite cell thickness, suggests that the new analysis can predict the mechanical response of ECs during AFM indentation better than Hertz's model, especially when using force-displacement data obtained from large indentations (>100 nm). The shear moduli and distensibility of ECs were greater when using small indentations (<100 nm) compared to large indentations (>100 nm). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced changes in the mechanical properties of ECs, which included a decrease in the average shear moduli that occurred in all regions of the ECs and an increase in distensibility in the central regions when measured using small indentations. These changes can be modeled as changes in a chain network structure within the ECs.
Figures






References
-
- Tajaddini, A., D. L. Kilpatrick, and D. G. Vince. 2003. A novel experimental method to estimate stress-strain behavior of intact coronary arteries using intravascular ultrasound (IVUS). J. Biomech. Eng. 125:120–123. - PubMed
-
- Kilpatrick, D., C. Xu, R. Vito, and S. Glagov. 2002. Correlation of mechanical behavior and MMP-1 presence in human atherosclerotic plaque. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2:1–7.
-
- Samani, A., and D. Plewes. 2004. A method to measure the hyperelastic parameters of ex vivo breast tissue samples. Phys. Med. Biol. 49:4395–4405. - PubMed
-
- Krouskop, T. A., T. M. Wheeler, F. Kallel, B. S. Garra, and T. Hall. 1998. Elastic moduli of breast and prostate tissues under compression. Ultrason. Imaging. 20:260–274. - PubMed
-
- Marchant, R. E., I. Kang, P. S. Sit, Y. Zhou, B. A. Todd, S. J. Eppell, and I. Lee. 2002. Molecular views and measurements of hemostatic processes using atomic force microscopy. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 3:249–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

