Phosphorylation by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 regulates the stability of transcription factor Sp1 during mitosis
- PMID: 18199680
- PMCID: PMC2262957
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-09-0881
Phosphorylation by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 regulates the stability of transcription factor Sp1 during mitosis
Abstract
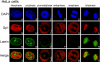
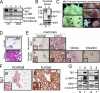
The transcription factor Sp1 is ubiquitously expressed in different cells and thereby regulates the expression of genes involved in many cellular processes. This study reveals that Sp1 was phosphorylated during the mitotic stage in three epithelial tumor cell lines and one glioma cell line. By using different kinase inhibitors, we found that during mitosis in HeLa cells, the c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) 1 was activated that was then required for the phosphorylation of Sp1. In addition, blockade of the Sp1 phosphorylation via inhibition JNK1 activity in mitosis resulted in the ubiquitination and degradation of Sp1. JNK1 phosphorylated Sp1 at Thr278/739. The Sp1 mutated at Thr278/739 was unstable during mitosis, possessing less transcriptional activity for the 12(S)-lipoxygenase expression and exhibiting a decreased cell growth rate compared with wild-type Sp1 in HeLa cells. In N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mammary tumors, JNK1 activation provided a potential relevance with the accumulation of Sp1. Together, our results indicate that JNK1 activation is necessary to phosphorylate Sp1 and to shield Sp1 from the ubiquitin-dependent degradation pathway during mitosis in tumor cell lines.
Figures






References
-
- Abdelrahim M., Safe S. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors decrease vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colon cancer cells by enhanced degradation of Sp1 and Sp4 proteins. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005;68:317–329. - PubMed
-
- Abdelrahim M., Smith R., 3rd, Burghardt R., Safe S. Role of Sp proteins in regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6740–6749. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong S. A., Barry D. A., Leggett R. W., Mueller C. R. Casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of the C terminus of Sp1 decreases its DNA binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:13489–13495. - PubMed
-
- Benasciutti E., Pages G., Kenzior O., Folk W., Blasi F., Crippa M. P. MAPK and JNK transduction pathways can phosphorylate Sp1 to activate the uPA minimal promoter element and endogenous gene transcription. Blood. 2004;104:256–262. - PubMed
-
- Bonello M. R., Khachigian L. M. Fibroblast growth factor-2 represses platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α (PDGFR-α) transcription via ERK1/2-dependent Sp1 phosphorylation and an atypical cis-acting element in the proximal PDGFR-α promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:2377–2382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

