Inhibition of p97-dependent protein degradation by Eeyarestatin I
- PMID: 18199748
- PMCID: PMC2276333
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M708347200
Inhibition of p97-dependent protein degradation by Eeyarestatin I
Abstract
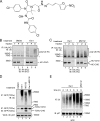
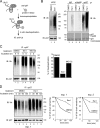
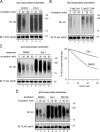
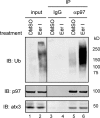
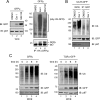
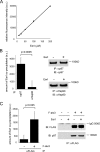
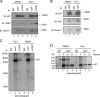
Elimination of misfolded proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by ER-associated degradation involves substrate retrotranslocation from the ER lumen into the cytosol for degradation by the proteasome. For many substrates, retrotranslocation requires the action of ubiquitinating enzymes, which polyubiquitinate substrates emerging from the ER lumen, and of the p97-Ufd1-Npl4 ATPase complex, which hydrolyzes ATP to dislocate polyubiquitinated substrates into the cytosol. Polypeptides extracted by p97 are eventually transferred to the proteasome for destruction. In mammalian cells, ERAD can be blocked by a chemical inhibitor termed Eeyarestatin I, but the mechanism of EerI action is unclear. Here we report that EerI can associate with a p97 complex to inhibit ERAD. The interaction of EerI with the p97 complex appears to negatively influence a deubiquitinating process that is mediated by p97-associated deubiquitinating enzymes. We further show that ataxin-3, a p97-associated deubiquitinating enzyme previously implicated in ER-associated degradation, is among those affected. Interestingly, p97-associated deubiquitination is also involved in degradation of a soluble substrate. Our analyses establish a role for a novel deubiquitinating process in proteasome-dependent protein turnover.
Figures
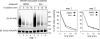
References
-
- Hampton, R. Y. (2002) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14 476–482 - PubMed
-
- Romisch, K. (2005) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 21 435–456 - PubMed
-
- Meusser, B., Hirsch, C., Jarosch, E., and Sommer, T. (2005) Nat. Cell Biol. 7 766–772 - PubMed
-
- Friedlander, R., Jarosch, E., Urban, J., Volkwein, C., and Sommer, T. (2000) Nat. Cell Biol. 2 379–384 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

