Revisiting the dialysate sodium prescription as a tool for better blood pressure and interdialytic weight gain management in hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 18199846
- PMCID: PMC6631087
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03360807
Revisiting the dialysate sodium prescription as a tool for better blood pressure and interdialytic weight gain management in hemodialysis patients
Abstract
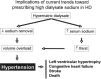
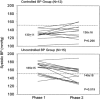
Hypertension and chronic volume overload are complications often seen in hemodialysis patients. Current hemodialysis practices adopt a standard dialysate sodium prescription that is typically higher than the plasma sodium concentration of most patients. As a general rule, hemodialysis patients have stable predialysis plasma sodium concentrations, and each patient has a fixed "osmolar set point." Hypertonic dialysate sodium prescriptions, including sodium modeling, predispose to positive sodium balance and lead to higher blood pressure and increased interdialytic weight gain. Conversely, lowering or individualizing dialysate sodium reduces thirst, interdialytic weight gain, and blood pressure in non-hypotension prone dialysis patients. Optimization of the dialysate sodium prescription is an important step in achieving sodium balance and improving blood pressure control in hypertensive hemodialysis patients.
Figures
References
-
- Santos SF, Peixoto AJ: Hypertension in dialysis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 14: 111–118, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Horl MP, Horl WH: Hemodialysis-associated hypertension: pathophysiology and therapy. Am J Kidney Dis 39: 227–244, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Flanigan MJ: Sodium flux and dialysate sodium in hemodialysis. Semin Dial 11: 298–304, 1998
-
- Flanigan MJ: Role of sodium in hemodialysis. Kidney Int Suppl 76[Suppl]: S72–S78, 2000 - PubMed
-
- de Paula FM, Peixoto AJ, Pinto LV, Dorigo D, Patricio PJ, Santos SF: Clinical consequences of an individualized dialysate sodium prescription in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 66: 1232–1238, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

