Polyfunctional T cell responses are a hallmark of HIV-2 infection
- PMID: 18200635
- PMCID: PMC2362391
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200737768
Polyfunctional T cell responses are a hallmark of HIV-2 infection
Abstract
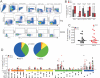
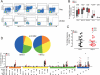
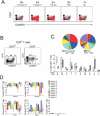
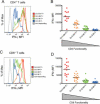
HIV-2 is distinguished clinically and immunologically from HIV-1 infection by delayed disease progression and maintenance of HIV-specific CD4(+) T cell help in most infected subjects. Thus, HIV-2 provides a unique natural human model in which to investigate correlates of immune protection against HIV disease progression. Here, we report a detailed assessment of the HIV-2-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell response compared to HIV-1, using polychromatic flow cytometry to assess the quality of the HIV-specific T cell response by measuring IFN-gamma, IL-2, TNF-alpha, MIP-1beta, and CD107a mobilization (degranulation) simultaneously following Gag peptide stimulation. We find that HIV-2-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells are more polyfunctional that those specific for HIV-1 and that polyfunctional HIV-2-specific T cells produce more IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha on a per-cell basis than monofunctional T cells. Polyfunctional HIV-2-specific CD4(+) T cells were generally more differentiated and expressed CD57, while there was no association between function and phenotype in the CD8(+) T cell fraction. Polyfunctional HIV-specific T cell responses are a hallmark of non-progressive HIV-2 infection and may be related to good clinical outcome in this setting.
Figures

References
-
- Poulsen AG, Aaby P, Larsen O, Jensen H, Naucler A, Lisse IM, Christiansen CB, et al. 9-year HIV-2-associated mortality in an urban community in Bissau, West Africa. Lancet. 1997;349:911–914. - PubMed
-
- Schim van der Loeff MF, Jaffar S, Aveika AA, Sabally S, Corrah T, Harding E, Alabi A, et al. Mortality of HIV-1, HIV-2 and HIV-1/HIV-2 dually infected patients in a clinic-based cohort in The Gambia. Aids. 2002;16:1775–1783. - PubMed
-
- Ariyoshi K, Jaffar S, Alabi AS, Berry N, Schim van der Loeff M, Sabally S, N'Gom PT, et al. Plasma RNA viral load predicts the rate of CD4 T cell decline and death in HIV-2-infected patients in West Africa. Aids. 2000;14:339–344. - PubMed
-
- Berry N, Jaffar S, Schim van der Loeff M, Ariyoshi K, Harding E, N'Gom PT, Dias F, et al. Low level viremia and high CD4% predict normal survival in a cohort of HIV type-2-infected villagers. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 2002;18:1167–1173. - PubMed
-
- Ariyoshi K, Berry N, Wilkins A, Ricard D, Aaby P, Naucler A, Ngom PT, et al. A community-based study of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 provirus load in rural village in West Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 1996;173:245–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

