Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 18200661
- PMCID: PMC2679127
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.390
Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
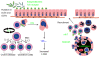
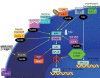
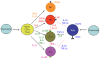
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are chronic relapsing immune mediated disorders that results from an aberrant response to gut luminal antigen in genetically susceptible host. The adaptive immune response that is then triggered was widely considered to be a T-helper-1 mediated condition in Crohn's disease and T-helper-2 mediated condition in ulcerative colitis. Recent studies in animal models, genome wide association, and basic science has provided important insights in in the immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease, one of which was the characterization of the interleukin-23/Th-17 axis.
Figures
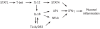
References
-
- Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science. 2005;307:1915–1920. - PubMed
-
- Seksik P, Sokol H, Lepage P, Vasquez N, Manichanh C, Mangin I, Pochart P, Dore J, Marteau P. Review article: the role of bacteria in onset and perpetuation of inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24 Suppl 3:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Colletti T. IBD--recognition, diagnosis, therapeutics. JAAPA. 2004;17:16–18, 21-24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

