Rheumatic heart disease: 15 years of clinical and immunological follow-up
- PMID: 18200819
- PMCID: PMC2350126
Rheumatic heart disease: 15 years of clinical and immunological follow-up
Abstract
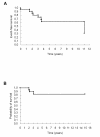
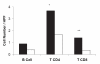
Rheumatic fever (RF) is a sequel of group A streptococcal throat infection and occurs in untreated susceptible children. Rheumatic heart disease (RHD), the major sequel of RF, occurs in 30%-45% of RF patients. RF is still considered endemic in some regions of Brazil and is responsible for approximately 90% of early childhood valvular surgery in the country. In this study, we present a 15-year clinical follow-up of 25 children who underwent surgical valvular repair. Histopathological and immunological features of heart tissue lesions of RHD patients were also evaluated. The patients presented severe forms of RHD with congestive symptoms at a very young age. Many of them had surgery at the acute phase of RF. Histological analysis showed the presence of dense valvular inflammatory infiltrates and Aschoff nodules in the myocardium of 21% of acute RHD patients. Infiltrating T-cells were mainly CD4+ in heart tissue biopsies of patients with rheumatic activity. In addition, CD4+ and CD8+ infiltrating T-cell clones recognized streptococcal M peptides and cardiac tissue proteins. These findings may open the possibilities of new ways of immunotherapy. In addition, we demonstrated that the surgical procedure during acute phase of the disease improved the quality of life of young RHD patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease: cellular mechanisms leading autoimmune reactivity and disease.J Clin Immunol. 2010 Jan;30(1):17-23. doi: 10.1007/s10875-009-9332-6. Epub 2009 Oct 3. J Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19802690 Review.
-
Molecular evidence for antigen-driven immune responses in cardiac lesions of rheumatic heart disease patients.Int Immunol. 2000 Jul;12(7):1063-74. doi: 10.1093/intimm/12.7.1063. Int Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10882418
-
How an autoimmune reaction triggered by molecular mimicry between streptococcal M protein and cardiac tissue proteins leads to heart lesions in rheumatic heart disease.J Autoimmun. 2005 Mar;24(2):101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2005.01.007. J Autoimmun. 2005. PMID: 15829402
-
T-cell reactivity against streptococcal antigens in the periphery mirrors reactivity of heart-infiltrating T lymphocytes in rheumatic heart disease patients.Infect Immun. 2001 Sep;69(9):5345-51. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.9.5345-5351.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11500404 Free PMC article.
-
Rheumatic fever: how S. pyogenes-primed peripheral T cells trigger heart valve lesions.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1051:132-40. doi: 10.1196/annals.1361.054. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16126952 Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies in the development of vaccines to prevent infections with group A streptococcus.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 Nov;9(11):2393-7. doi: 10.4161/hv.25506. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23863455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidental Diagnosis of Rheumatic Myocarditis during Cardiac Surgery-Impact on Late Prognosis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;13(20):3252. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13203252. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892073 Free PMC article.
-
Incidental histological diagnosis of acute rheumatic myocarditis: case report and review of the literature.Front Pediatr. 2014 Nov 20;2:126. doi: 10.3389/fped.2014.00126. eCollection 2014. Front Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 25478552 Free PMC article.
-
StreptInCor, a Group A Streptococcal Adsorbed Vaccine: Evaluation of Repeated Intramuscular Dose Toxicity Testing in Rats.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 May 11;8:643317. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.643317. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34046438 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 4: Its Role in Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Valvular, and Nonvalvular Cardiovascular Diseases.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Jan;25(1):7-14. doi: 10.1177/1074248419868699. Epub 2019 Aug 11. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31401864 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abou-Zeid C, Filley E, Steele J, et al. A simple new method for using antigens separeted by polyacrilamide gel electrophoresis to stimulate lymphocites “in vitro” after converting bands cut from Western blots into antigen-bearing particles. J Immunol Methods. 1987;98:5–10. - PubMed
-
- Carapetis JR, McDonald M, Wilson NJ. Acute rheumatic fever. Lancet. 2005;366:155–68. - PubMed
-
- Carapetis JR, Steer AC, Mulholland EK, et al. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:685–94. - PubMed
-
- Carapetis JR, Mayosi BM, Kaplan EL. Controlling rheumatic heart disease in developing countries. Cardiovasc JS Afr. 2006;17:164–65. - PubMed
-
- Cohen IR. T-cell vaccination for autoimmune disease: a panorama. Vaccine. 2002;20:706–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

