Adjuvant modulation of the cytokine balance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis subunit vaccines; immunity, pathology and protection
- PMID: 18201185
- PMCID: PMC2566622
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02751.x
Adjuvant modulation of the cytokine balance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis subunit vaccines; immunity, pathology and protection
Abstract
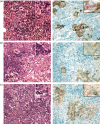
It is known that protection against tuberculosis is mediated primarily by T helper type 1 (Th1) cells but the influence of the Th1/Th2 balance of a vaccination response on the subsequent protection and pathology during infection has not been studied in detail. We designed a panel of Ag85B-ESAT-6 subunit vaccines based on adjuvants with different Th1/Th2-promoting activities and studied cellular responses, bacterial replication and pathology in the lungs of mice infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. All vaccines induced cell-mediated and humoral responses but with markedly different interferon-gamma : interleukin-5 (IFN-gamma : IL-5) and immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) : IgG2 ratios. The vaccines promoted different levels of control of bacterial replication with the most efficient protection being exerted by cationic liposomes containing monophosphoryl lipid A and low to completely absent immunity with conventional aluminium. The level of protection correlated with the amount of IFN-gamma produced in response to the vaccine whereas there was no inverse correlation with the level of IL-5. Characterizing a protective response was an accelerated recruitment of IL-17 and IFN-gamma-producing lymphocytes resulting in the early formation of granulomas containing clustered inducible nitric oxide synthase-activated macrophages. In comparison, non-protected mice exhibited a different inflammatory infiltrate rich in neutrophil granulocytes. This study indicates that the adjuvant component of a tuberculosis vaccine may be crucial in determining the kinetics by which effective granulomas, pivotal in controlling bacterial growth, are formed.
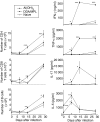
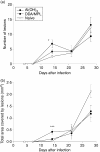
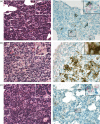
Figures
References
-
- Jouanguy E, Altare F, Lamhamedi S, et al. Interferon-gamma-receptor deficiency in an infant with fatal bacille Calmette–Guérin infection. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1956–61. - PubMed
-
- Remiszewski P, Roszkowska SLB, Winek J, et al. Disseminated Mycobacterium avium infection in a 20-year-old female with partial recessive IFNgammaR1 deficiency. Respiration. 2006;73:375–8. - PubMed
-
- Andersen P, Doherty TM. TB subunit vaccines – putting the pieces together. Microbes Infect. 2005;7:911–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

