Limb remote-preconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats and contradicts the dogma of therapeutic time windows for preconditioning
- PMID: 18201834
- PMCID: PMC2696348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.11.056
Limb remote-preconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats and contradicts the dogma of therapeutic time windows for preconditioning
Abstract
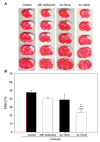
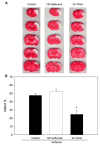
Remote ischemic preconditioning is an emerging concept for stroke treatment, but its protection against focal stroke has not been established. We tested whether remote preconditioning, performed in the ipsilateral hind limb, protects against focal stroke and explored its protective parameters. Stroke was generated by a permanent occlusion of the left distal middle cerebral artery (MCA) combined with a 30 min occlusion of the bilateral common carotid arteries (CCA) in male rats. Limb preconditioning was generated by 5 or 15 min occlusion followed with the same period of reperfusion of the left hind femoral artery, and repeated for two or three cycles. Infarct was measured 2 days later. The results showed that rapid preconditioning with three cycles of 15 min performed immediately before stroke reduced infarct size from 47.7+/-7.6% of control ischemia to 9.8+/-8.6%; at two cycles of 15 min, infarct was reduced to 24.7+/-7.3%; at two cycles of 5 min, infarct was not reduced. Delayed preconditioning with three cycles of 15 min conducted 2 days before stroke also reduced infarct to 23.0+/-10.9%, but with two cycles of 15 min it offered no protection. The protective effects at these two therapeutic time windows of remote preconditioning are consistent with those of conventional preconditioning, in which the preconditioning ischemia is induced in the brain itself. Unexpectedly, intermediate preconditioning with three cycles of 15 min performed 12 h before stroke also reduced infarct to 24.7+/-4.7%, which contradicts the current dogma for therapeutic time windows for the conventional preconditioning that has no protection at this time point. In conclusion, remote preconditioning performed in one limb protected against ischemic damage after focal cerebral ischemia.
Figures


References
-
- Birnbaum Y, Hale SL, Kloner RA. Ischemic preconditioning at a distance: reduction of myocardial infarct size by partial reduction of blood supply combined with rapid stimulation of the gastrocnemius muscle in the rabbit. Circulation. 1997;96:1641–1646. - PubMed
-
- Dave KR, Saul I, Prado R, Busto R, Perez-Pinzon MA. Remote organ ischemic preconditioning protect brain from ischemic damage following asphyxial cardiac arrest. Neurosci Lett. 2006;404:170–175. - PubMed
-
- Gidday JM. Cerebral preconditioning and ischaemic tolerance. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:437–448. - PubMed
-
- Jin RL, Li WB, Li QJ, Zhang M, Xian XH, Sun XC, Zhao HG, Qi J. The role of extracellular signal-regulated kinases in the neuroprotection of limb ischemic preconditioning. Neurosci Res. 2006;55:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Kakimoto M, Kawaguchi M, Sakamoto T, Inoue S, Furuya H, Nakamura M, Konishi N. Evaluation of rapid ischemic preconditioning in a rabbit model of spinal cord ischemia. Anesthesiology. 2003;99:1112–1117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

