Epigenetic regulation of kappa opioid receptor gene in neuronal differentiation
- PMID: 18201839
- PMCID: PMC2265776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.12.015
Epigenetic regulation of kappa opioid receptor gene in neuronal differentiation
Abstract
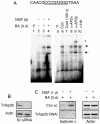
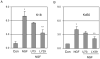
The gene of mouse kappa opioid receptor (KOR) utilizes two promoters, P1 and P2. P1 is active in various brain areas and constitutively in P19 mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. P2 is active in limited brain stem areas of adult animals and only in late differentiated cells of P19 induced for neuronal differentiation in the presence of nerve growth factor (NGF). NGF response of P2 was found to be mediated by a specific binding site for transcription factor activation protein 2 (AP2) located in P2. Electrophoretic gel shift assay showed specific binding of this AP2 site by AP2beta, but not AP2alpha. Knockdown of endogenous AP2beta with siRNA abolished the stimulating effect of NGF on the expression of transcripts driven by P2. Binding of endogenous AP2beta on the endogenous KOR P2 chromatin region was also confirmed by chromatin immunoprecipitation. The effect of NGF was inhibited by LY2942002 (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, PI3K inhibitor), suggesting that PI3K was involved in signaling pathway mediating the effect of NGF stimulation on KOR P2. The chromatin of P2 in P19 was found to be specifically modified following NGF stimulation, which included demethylation at Lys9 and dimethylation at Lys4 of histone H3 and was consistent with the increased recruitment of RNA polymerase II to this promoter. This study presents the first evidence for epigenetic changes occurred on a specific KOR promoter triggered by NGF in cells undergoing neuronal differentiation. This epigenetic change is mediated by recruited AP2beta to this promoter and involves the PI3K system.
Figures





References
-
- Appleyard SM, Patterson TA, Jin W, Chavkin C. Agonist-induced phosphorylation of the κ-opioid receptor. J Neurochem. 1997;69:2405–2412. - PubMed
-
- Arden JR, Segredo V, Wang Z, Lameh J, Sadée W. Phosphorylation and agonist-specific intracellular trafficking of an epitope-tagged μ-opioid receptor expressed in HEK 293 cells. J Neurochem. 1995;65:1636–1645. - PubMed
-
- Bi J, Hu X, Loh HH, Wei LN. Mouse κ-opioid receptor mRNA differential transport in neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64:594–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK060521/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA11190/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DK54733/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA013926/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02-DA13926/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA001583/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA001583/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DK60521/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA011190/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05-DA070554/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054733/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA070554/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA11806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

