Comparison of vascular endothelial growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 in a swine model of endothelial dysfunction
- PMID: 18201892
- PMCID: PMC2329802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2007.12.016
Comparison of vascular endothelial growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 in a swine model of endothelial dysfunction
Abstract
Objective: Growth factor based angiogenesis, with or without cell therapy, is a promising therapeutic modality for patients with coronary artery disease. We compared the relative efficacies of surgically delivered vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) in a swine model of hypercholesterolemia-induced endothelial dysfunction which captures many of the pathophysiologic abnormalities of human coronary disease.
Methods: Yucatan mini-swine (20-30 kg), fed a high cholesterol diet (total 20 weeks), underwent circumflex ameroid placement to create chronic myocardial ischemia, followed three weeks later by perivascular administration of VEGF (2 microg; n=6), FGF-2 (100 microg; n=6), or placebo (n=7) in the ischemic territory. Normocholesterolemic animals (n=7) served as controls. Four weeks later, endothelial function, collateral-dependent perfusion, as well as myocardial protein and mRNA levels of angiogenic mediators were assessed.
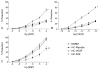
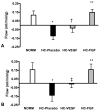
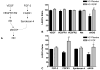
Results: Endothelial dysfunction was observed in all hypercholesterolemic animals as impaired microvessel relaxation in response to adenosine diphosphate and VEGF. VEGF administration improved baseline-adjusted collateral-dependent perfusion at rest (-0.03+/-0.05 vs -0.12+/-0.04, VEGF vs placebo, p=0.09), but FGF-2 delivery caused a significantly greater improvement in perfusion compared to either group (+0.15+/-0.03, p<0.05 vs HC-placebo and HC-VEGF) at rest. Molecular analysis revealed increased eNOS expression (135%+/-8%, p=0.03 vs placebo) in all growth factor treated animals and increased expression of FGF-2 receptor, FGFR1 (65+/-26%, p=0.04 vs placebo), in FGF-2 treated animals. No significant changes were demonstrated in other angiogenic mediators including Akt, Syndecan-4.
Conclusions: In the setting of hypercholesterolemic endothelial dysfunction, FGF-2 is more effective than VEGF at enhancing collateral-dependent perfusion and thus, may be a better candidate than VEGF for angiogenic therapy in patients with end-stage CAD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-dose atorvastatin is associated with impaired myocardial angiogenesis in response to vascular endothelial growth factor in hypercholesterolemic swine.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006 Dec;132(6):1299-306. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2006.05.060. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006. PMID: 17140946
-
High-dose atorvastatin improves hypercholesterolemic coronary endothelial dysfunction without improving the angiogenic response.Circulation. 2006 Jul 4;114(1 Suppl):I402-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.000356. Circulation. 2006. PMID: 16820608
-
Effects of L-arginine on fibroblast growth factor 2-induced angiogenesis in a model of endothelial dysfunction.Circulation. 2005 Aug 30;112(9 Suppl):I202-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.526350. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 16159817
-
Therapeutic angiogenesis for coronary artery disease.Ann Intern Med. 2002 Jan 1;136(1):54-71. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-1-200201010-00011. Ann Intern Med. 2002. PMID: 11777364 Review.
-
Therapeutic angiogenesis in cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003 Nov;2(11):863-71. doi: 10.1038/nrd1226. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003. PMID: 14668807 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Related transcriptional enhancer factor 1 increases endothelial-dependent microvascular relaxation and proliferation.J Vasc Res. 2012;49(3):249-59. doi: 10.1159/000335180. Epub 2012 Mar 15. J Vasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22433836 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cyclooxygenase inhibition on cardiovascular function in a hypercholesterolemic swine model of chronic ischemia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Jan;302(2):H479-88. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00146.2011. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22037194 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial therapeutic angiogenesis: a review of the state of development and future obstacles.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2011 Nov;9(11):1469-79. doi: 10.1586/erc.11.148. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2011. PMID: 22059795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-angiogenic effect of high-dose resveratrol in a swine model of metabolic syndrome.Surgery. 2010 Aug;148(2):453-62. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2010.04.013. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Surgery. 2010. PMID: 20570307 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal and spatial changes in collateral formation and function during chronic myocardial ischemia.J Am Coll Surg. 2010 Oct;211(4):470-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.06.009. Epub 2010 Aug 21. J Am Coll Surg. 2010. PMID: 20729101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simons M, Bonow RO, Chronos NA, Cohen DJ, Giordano FJ, Hammond HK, Laham RJ, Li W, Pike M, Sellke FW, Stegmann TJ, Udelson JE, Rosengart TK. Clinical trials in coronary angiogenesis: issues, problems, consensus: An expert panel summary. Circulation. 2000;102:E73–86. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653–660. - PubMed
-
- Boodhwani M, Sodha NR, Laham RJ, Sellke FW. The future of therapeutic myocardial angiogenesis. Shock. 2006;26:332–341. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Zhao SP, Li XP, Gao M, Zhou QC. Endothelium-dependent and -independent functions are impaired in patients with coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis. 2000;149:19–24. - PubMed
-
- Boodhwani M, Nakai Y, Mieno S, Voisine P, Bianchi C, Araujo EG, Feng J, Michael K, Li J, Sellke FW. Hypercholesterolemia impairs the myocardial angiogenic response in a swine model of chronic ischemia: role of endostatin and oxidative stress. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81:634–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

