Cooperative control via lymphoid enhancer factor 1/T cell factor 3 and estrogen receptor-alpha for uterine gene regulation by estrogen
- PMID: 18202148
- PMCID: PMC2366180
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2007-0445
Cooperative control via lymphoid enhancer factor 1/T cell factor 3 and estrogen receptor-alpha for uterine gene regulation by estrogen
Abstract
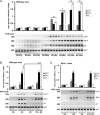
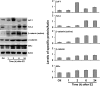
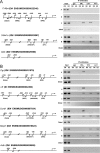
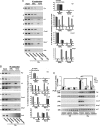
Accumulating evidence indicates that estrogen regulates diverse but interdependent signaling pathways via estrogen receptor (ER)-dependent and -independent mechanisms. However, molecular relationship between these pathways for gene regulation under the direction of estrogen remains unknown. To address this possibility, our uterine analysis of Wnt/beta-catenin downstream effectors revealed that lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (Lef-1) and T cell factor 3 (Tcf-3) are up-regulated temporally by 17beta-estradiol (E2) in an ER-independent manner. Lef-1 is abundantly up-regulated early (within 2 h), whereas Tcf-3 is predominantly induced after 6 h, and both are sustained through 24 h. Interestingly, activated Lef-1/Tcf-3 molecularly interacted with ERalpha in a time-dependent manner, suggesting they possess a cross talk in the uterus by E2. Moreover, dual immunofluorescence studies confirm their colocalization in uterine epithelial cells after E2. Most importantly, using chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by PCR analyses, we provide evidence for an interesting possibility that ERalpha and Tcf-3/Lef-1 complex occupies at certain DNA regions of estrogen-responsive endogenous gene promoters in the mouse uterus. By selective perturbation of activated Lef-1/Tcf-3 or ERalpha signaling events, we provide in this study novel evidence that cooperative interactions, by these two different classes of transcription factors at the level of chromatin, direct uterine regulation of estrogen-responsive genes. Collectively, these studies support a mechanism that integration of a nonclassically induced beta-catenin/Lef-1/Tcf-3 signaling with ERalpha is necessary for estrogen-dependent endogenous gene regulation in uterine biology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A distal super enhancer mediates estrogen-dependent mouse uterine-specific gene transcription of Igf1 (insulin-like growth factor 1).J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 21;294(25):9746-9759. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008759. Epub 2019 May 9. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31073032 Free PMC article.
-
GPR30 activation opposes estrogen-dependent uterine growth via inhibition of stromal ERK1/2 and estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) phosphorylation signals.Endocrinology. 2011 Apr;152(4):1434-47. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-1368. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21303939 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression patterns of Wnt and beta-catenin/TCF target genes in the uterus of immature female rats exposed to 17alpha-ethynyl estradiol.Toxicol Sci. 2006 Jun;91(2):419-30. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfj167. Epub 2006 Mar 21. Toxicol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16551644
-
The role of LEF/TCF factors in neoplastic transformation.Curr Mol Med. 2008 Feb;8(1):38-50. doi: 10.2174/156652408783565559. Curr Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18289012 Review.
-
Diversity of LEF/TCF action in development and disease.Oncogene. 2006 Dec 4;25(57):7492-504. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210056. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 17143293 Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse primary uterine cell coculture system revisited: ovarian hormones mimic the aspects of in vivo uterine cell proliferation.Endocrinology. 2011 Aug;152(8):3246-58. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-0223. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21693674 Free PMC article.
-
Selective disruption of ER{alpha} DNA-binding activity alters uterine responsiveness to estradiol.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Dec;23(12):2111-6. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0356. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19812388 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-mediated regulation of Igf1 transcription and uterine growth involves direct binding of estrogen receptor alpha to estrogen-responsive elements.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 22;285(4):2676-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.043471. Epub 2009 Nov 17. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19920132 Free PMC article.
-
Research resource: whole-genome estrogen receptor α binding in mouse uterine tissue revealed by ChIP-seq.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 May;26(5):887-98. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1311. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22446102 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of uterine estrogen signaling during early pregnancy in mice: an update.J Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Apr;56(3):R127-38. doi: 10.1530/JME-15-0300. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26887389 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Couse JF, Korach KS 1999 Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev 20:358–417 - PubMed
-
- Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Speizer FE, Hennekens CH 1991 Postmenopausal estrogen therapy and cardiovascular disease. Ten-year follow-up from the nurses' health study. N Engl J Med 325:756–762 - PubMed
-
- McDonnell DP, Norris JD 2002 Connections and regulation of the human estrogen receptor. Science 296:1642–1644 - PubMed
-
- Dey SK, Lim H, Das SK, Reese J, Paria BC, Daikoku T, Wang H 2004 Molecular cues to implantation. Endocr Rev 25:341–373 - PubMed
-
- Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW 1994 Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem 63:451–486 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

