Cooperative control via lymphoid enhancer factor 1/T cell factor 3 and estrogen receptor-alpha for uterine gene regulation by estrogen
- PMID: 18202148
- PMCID: PMC2366180
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2007-0445
Cooperative control via lymphoid enhancer factor 1/T cell factor 3 and estrogen receptor-alpha for uterine gene regulation by estrogen
Abstract
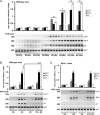
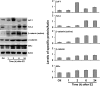
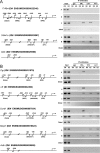
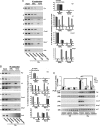
Accumulating evidence indicates that estrogen regulates diverse but interdependent signaling pathways via estrogen receptor (ER)-dependent and -independent mechanisms. However, molecular relationship between these pathways for gene regulation under the direction of estrogen remains unknown. To address this possibility, our uterine analysis of Wnt/beta-catenin downstream effectors revealed that lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (Lef-1) and T cell factor 3 (Tcf-3) are up-regulated temporally by 17beta-estradiol (E2) in an ER-independent manner. Lef-1 is abundantly up-regulated early (within 2 h), whereas Tcf-3 is predominantly induced after 6 h, and both are sustained through 24 h. Interestingly, activated Lef-1/Tcf-3 molecularly interacted with ERalpha in a time-dependent manner, suggesting they possess a cross talk in the uterus by E2. Moreover, dual immunofluorescence studies confirm their colocalization in uterine epithelial cells after E2. Most importantly, using chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by PCR analyses, we provide evidence for an interesting possibility that ERalpha and Tcf-3/Lef-1 complex occupies at certain DNA regions of estrogen-responsive endogenous gene promoters in the mouse uterus. By selective perturbation of activated Lef-1/Tcf-3 or ERalpha signaling events, we provide in this study novel evidence that cooperative interactions, by these two different classes of transcription factors at the level of chromatin, direct uterine regulation of estrogen-responsive genes. Collectively, these studies support a mechanism that integration of a nonclassically induced beta-catenin/Lef-1/Tcf-3 signaling with ERalpha is necessary for estrogen-dependent endogenous gene regulation in uterine biology.
Figures



References
-
- Couse JF, Korach KS 1999 Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev 20:358–417 - PubMed
-
- Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Speizer FE, Hennekens CH 1991 Postmenopausal estrogen therapy and cardiovascular disease. Ten-year follow-up from the nurses' health study. N Engl J Med 325:756–762 - PubMed
-
- McDonnell DP, Norris JD 2002 Connections and regulation of the human estrogen receptor. Science 296:1642–1644 - PubMed
-
- Dey SK, Lim H, Das SK, Reese J, Paria BC, Daikoku T, Wang H 2004 Molecular cues to implantation. Endocr Rev 25:341–373 - PubMed
-
- Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW 1994 Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem 63:451–486 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

