Repositioning of an alternative exon sequence of mouse IgM pre-mRNA activates splicing of the preceding intron
- PMID: 1820216
- PMCID: PMC5952188
Repositioning of an alternative exon sequence of mouse IgM pre-mRNA activates splicing of the preceding intron
Abstract
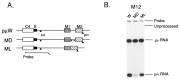
Using a transient expression system of mouse IgM mini-gene constructs in mouse B-cell lines and in fibroblast L cell, we investigated splicing of the IgM transcript. We observed that the efficiency of splicing between exons C4 and M1 (C4-to-M1 splicing), the splicing reaction leading to the production of membrane-bound form (microns) mRNA, was drastically affected by mutations in a specific portion of the downstream exon (M2). The results show that the specific exon M2 sequence activates the C4-to-M1 splicing. This activation was not observed when splicing between exons M1 and M2 was abolished by base substitutions at the splice sites. These results indicate that positioning of the downstream exon is crucial for efficient splicing of the preceding intron.
Figures
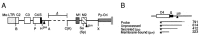



References
-
- Alt F. W., Bothwell A. L. M., Knapp M., Siden E., Mather E., Koshland M., and Baltimore D. (1980), Cell 20, 293–301. - PubMed
-
- Bell L. R., Maine E. M., Schedl P. and Cline T. W. (1988), Cell 55, 1037–1046. - PubMed
-
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., and Nadal-Ginard B. (1987), Annu Rev Biochem 56, 467–495. - PubMed
-
- Brody E. and Abelson J. (1985), Science 228, 963–967. - PubMed
-
- Burtis K. C. and Baker B. S. (1989), Cell 56, 997–1010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
