Disrupted membrane homeostasis and accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins in a mouse model of infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy caused by PLA2G6 mutations
- PMID: 18202189
- PMCID: PMC2312364
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070823
Disrupted membrane homeostasis and accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins in a mouse model of infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy caused by PLA2G6 mutations
Abstract
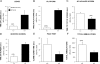
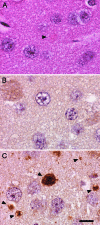
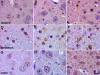
Mutations in the PLA2G6 gene, which encodes group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA(2)beta), were recently identified in patients with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD) and neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. A pathological hallmark of these childhood neurodegenerative diseases is the presence of distinctive spheroids in distal axons that contain accumulated membranes. We used iPLA(2)beta-KO mice generated by homologous recombination to investigate neurodegenerative consequences of PLA2G6 mutations. iPLA(2)beta-KO mice developed age-dependent neurological impairment that was evident in rotarod, balance, and climbing tests by 13 months of age. The primary abnormality underlying this neurological impairment was the formation of spheroids containing tubulovesicular membranes remarkably similar to human INAD. Spheroids were strongly labeled with anti-ubiquitin antibodies. Accumulation of ubiquitinated protein in spheroids was evident in some brain regions as early as 4 months of age, and the onset of motor impairment correlated with a dramatic increase in ubiquitin-positive spheroids throughout the neuropil in nearly all brain regions. Furthermore accumulating ubiquitinated proteins were observed primarily in insoluble fractions of brain tissue, implicating protein aggregation in this pathogenic process. These results indicate that loss of iPLA(2)beta causes age-dependent impairment of axonal membrane homeostasis and protein degradation pathways, leading to age-dependent neurological impairment. iPLA(2)beta-KO mice will be useful for further studies of pathogenesis and experimental interventions in INAD and neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation.
Figures


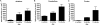


Similar articles
-
Establishment of an improved mouse model for infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy that shows early disease onset and bears a point mutation in Pla2g6.Am J Pathol. 2009 Dec;175(6):2257-63. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090343. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19893029 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroaxonal dystrophy in PLA2G6 knockout mice.Neuropathology. 2015 Jun;35(3):289-302. doi: 10.1111/neup.12202. Epub 2015 May 6. Neuropathology. 2015. PMID: 25950622 Review.
-
A new PLA2G6 mutation in a family with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy.J Neurol Sci. 2017 Oct 15;381:209-212. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2017.08.3260. Epub 2017 Sep 1. J Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28991683
-
Neuroaxonal dystrophy in calcium-independent phospholipase A2β deficiency results from insufficient remodeling and degeneration of mitochondrial and presynaptic membranes.J Neurosci. 2011 Aug 3;31(31):11411-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0345-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21813701 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of human INAD by Pla2g6 deficiency.Histol Histopathol. 2013 Aug;28(8):965-9. doi: 10.14670/HH-28.965. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Histol Histopathol. 2013. PMID: 23467909 Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium-independent phospholipases A2 and their roles in biological processes and diseases.J Lipid Res. 2015 Sep;56(9):1643-68. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R058701. Epub 2015 May 28. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 26023050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PLA2G6-Associated Neurodegeneration (PLAN): Review of Clinical Phenotypes and Genotypes.Front Neurol. 2018 Dec 18;9:1100. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.01100. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30619057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of PLA2G6 in human fetal development: Implications for infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy.Brain Res Bull. 2010 Nov 20;83(6):374-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2010.08.011. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Brain Res Bull. 2010. PMID: 20813170 Free PMC article.
-
Defective lipid metabolism in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) syndromes: not only a matter of iron.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015 Jan;38(1):123-36. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9770-z. Epub 2014 Oct 10. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015. PMID: 25300979 Review.
-
Excess iron harms the brain: the syndromes of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA).J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2013 Apr;120(4):695-703. doi: 10.1007/s00702-012-0922-8. Epub 2012 Dec 2. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2013. PMID: 23212724 Review.
References
-
- Kimura S. Terminal axon pathology in infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. Pediatr Neurol. 1991;7:116–120. - PubMed
-
- Yagishita S, Kimura S. Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. Histological and electron microscopical study of two cases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1974;29:115–126. - PubMed
-
- de Leon GA, Mitchell MH. Histological and ultrastructural features of dystrophic isocortical axons in infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (Seitelberger’s disease). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1985;66:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Yagishita S, Kimura S. Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (Seitelberger’s disease). A light and ultrastructural study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1975;31:191–200. - PubMed
-
- Liu HM, Larson M, Mizuno Y. An analysis of the ultrastructural findings in infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (Seitelberger’s disease). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1974;27:201–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK034388/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37-DK34388/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS48924-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS048924/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P60-DK20579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5P01HL57278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41-RR00954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK56341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

