Angiopoietin-like 5 and IGFBP2 stimulate ex vivo expansion of human cord blood hematopoietic stem cells as assayed by NOD/SCID transplantation
- PMID: 18202223
- PMCID: PMC2275010
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-11-122119
Angiopoietin-like 5 and IGFBP2 stimulate ex vivo expansion of human cord blood hematopoietic stem cells as assayed by NOD/SCID transplantation
Abstract
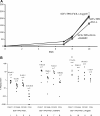
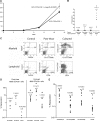
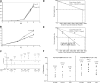
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the basis of bone marrow transplantation and are attractive target cells for hematopoietic gene therapy, but these important clinical applications have been severely hampered by difficulties in ex vivo expansion of HSCs. In particular, the use of cord blood for adult transplantation is greatly limited by the number of HSCs. Previously we identified angiopoietin-like proteins and IGF-binding protein 2 (IGFBP2) as new hormones that, together with other factors, can expand mouse bone marrow HSCs in culture. Here, we measure the activity of multipotent human severe combined immunodeficient (SCID)-repopulating cells (SRCs) by transplantation into the nonobese diabetic SCID (NOD/SCID) mice; secondary transplantation was performed to evaluate the self-renewal potential of SRCs. A serum-free medium containing SCF, TPO, and FGF-1 or Flt3-L cannot significantly support expansion of the SRCs present in human cord blood CD133+ cells. Addition of either angiopoietin-like 5 or IGF-binding protein 2 to the cultures led to a sizable expansion of HSC numbers, as assayed by NOD/SCID transplantation. A serum-free culture containing SCF, TPO, FGF-1, angiopoietin-like 5, and IGFBP2 supports an approximately 20-fold net expansion of repopulating human cord blood HSCs, a number potentially applicable to several clinical processes including HSC transplantation.
Figures

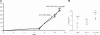
References
-
- Sauvageau G, Iscove NN, Humphries RK. In vitro and in vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:7223–7232. - PubMed
-
- Kirouac DC, Zandstra PW. Understanding cellular networks to improve hematopoietic stem cell expansion cultures. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2006;17:538–547. - PubMed
-
- Brunstein CG, Wagner JE. Umbilical cord blood transplantation and banking. Annu Rev Med. 2006;57:403–417. - PubMed
-
- Robinson S, Niu T, de Lima M, et al. Ex vivo expansion of umbilical cord blood. Cytotherapy. 2005;7:243–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

