Clonal integration of a polyomavirus in human Merkel cell carcinoma
- PMID: 18202256
- PMCID: PMC2740911
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1152586
Clonal integration of a polyomavirus in human Merkel cell carcinoma
Abstract
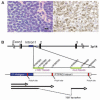
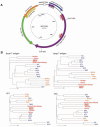
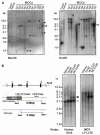
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare but aggressive human skin cancer that typically affects elderly and immunosuppressed individuals, a feature suggestive of an infectious origin. We studied MCC samples by digital transcriptome subtraction and detected a fusion transcript between a previously undescribed virus T antigen and a human receptor tyrosine phosphatase. Further investigation led to identification and sequence analysis of the 5387-base-pair genome of a previously unknown polyomavirus that we call Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV or MCPyV). MCV sequences were detected in 8 of 10 (80%) MCC tumors but only 5 of 59 (8%) control tissues from various body sites and 4 of 25 (16%) control skin tissues. In six of eight MCV-positive MCCs, viral DNA was integrated within the tumor genome in a clonal pattern, suggesting that MCV infection and integration preceded clonal expansion of the tumor cells. Thus, MCV may be a contributing factor in the pathogenesis of MCC.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cancer. A skin cancer virus?Science. 2008 Feb 22;319(5866):1049-50. doi: 10.1126/science.1155048. Science. 2008. PMID: 18292327 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

