Chemical approaches to understanding O-GlcNAc glycosylation in the brain
- PMID: 18202679
- PMCID: PMC3250351
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.68
Chemical approaches to understanding O-GlcNAc glycosylation in the brain
Abstract
O-GlcNAc glycosylation is a unique, dynamic form of glycosylation found on intracellular proteins of all multicellular organisms. Studies suggest that O-GlcNAc represents a key regulatory modification in the brain, contributing to transcriptional regulation, neuronal communication and neurodegenerative disease. Recently, several new chemical tools have been developed to detect and study the modification, including chemoenzymatic tagging methods, quantitative proteomics strategies and small-molecule inhibitors of O-GlcNAc enzymes. Here we highlight some of the emerging roles for O-GlcNAc in the nervous system and describe how chemical tools have significantly advanced our understanding of the scope, functional significance and cellular dynamics of this modification.
Figures
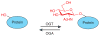




References
-
- Torres CR, Hart GW. Topography and polypeptide distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine residues on the surfaces of intact lymphocytes. Evidence for O-linked GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:3308–3317. - PubMed
-
- Love DC, Hanover JA. The hexosamine signaling pathway: deciphering the ‘O-GlcNAc code’. Sci STKE. 2005;2005:re13. - PubMed
-
- Roquemore EP, Chevrier MR, Cotter RJ, Hart GW. Dynamic O-GlcNAcylation of the small heat shock protein αB-crystallin. Biochemistry. 1996;35:3578–3586. - PubMed
-
- Comer FI, Hart GW. O-GlcNAc and the control of gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1473:161–171. - PubMed
-
- Zachara NE, Hart GW. O-GlcNAc a sensor of cellular state: the role of nucleo-cytoplasmic glycosylation in modulating cellular function in response to nutrition and stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1673:13–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

