Detection of peritoneal metastases
- PMID: 18203670
- PMCID: PMC4448957
- DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2001.002
Detection of peritoneal metastases
Abstract
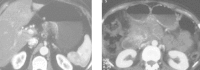
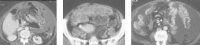
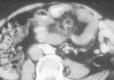
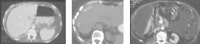
The peritoneum is the largest and most complexly arranged serious membrane in the body. The potential peritoneal spaces, the peritoneal reflections forming peritoneal ligaments, mesenteries, omenta, and the natural flow of peritoneal fluid determine the route of spread of intraperitoneal fluid and consequently disease spread within the abdominal cavity. The peritoneal ligaments, mesenteries, and omenta also serve as boundaries and conduits for disease spread. Peritoneal metastases spread in four ways: (1) Direct spread along peritoneal ligaments, mesenteries and omenta to non-contiguous organs; (2) Intraperitoneal seeding via ascitic fluid; (3) Lymphatic extension; (4) Embolic haematogenous spread. Before the introduction of cross-sectional imaging, the peritoneum and its reflections could only be imaged with difficulty, often requiring invasive techniques. Computed tomography and to a lesser extent sonography and MR imaging allow us to examine the complex anatomy of the peritoneal cavity accurately, which is the key to understanding the spread of peritoneal disease. This article reviews the detection of peritoneal metastases.
Figures

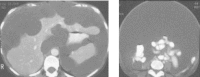
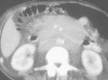
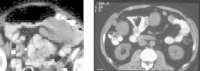
Similar articles
-
The peritoneum, mesenteries and omenta: normal anatomy and pathological processes.Eur Radiol. 1998;8(6):886-900. doi: 10.1007/s003300050485. Eur Radiol. 1998. PMID: 9683690 Review.
-
Peritoneal and retroperitoneal anatomy and its relevance for cross-sectional imaging.Radiographics. 2012 Mar-Apr;32(2):437-51. doi: 10.1148/rg.322115032. Radiographics. 2012. PMID: 22411941 Review.
-
Patterns of peritoneal spread of tumor in the abdomen and pelvis.World J Radiol. 2013 Mar 28;5(3):106-12. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i3.106. World J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23671747 Free PMC article.
-
Greater and lesser omenta: normal anatomy and pathologic processes.Radiographics. 2007 May-Jun;27(3):707-20. doi: 10.1148/rg.273065085. Radiographics. 2007. PMID: 17495288 Review.
-
Anatomic CT demonstration of the peritoneal spaces, ligaments, and mesenteries: normal and pathologic processes.Radiographics. 1995 Jul;15(4):755-70. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.15.4.7569127. Radiographics. 1995. PMID: 7569127 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic review of diagnostic tools for peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer-staging laparoscopy and its alternatives.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 Oct 27;15(10):2280-2293. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i10.2280. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023. PMID: 37969710 Free PMC article.
-
Alginate Microsphere Encapsulation of Drug-Loaded Nanoparticles: A Novel Strategy for Intraperitoneal Drug Delivery.Mar Drugs. 2022 Nov 26;20(12):744. doi: 10.3390/md20120744. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36547891 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Gallbladder Width Measurement by Computed Tomography in the Diagnosis of Acute Cholecystitis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 16;12(3):721. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030721. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328274 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-therapy CT scan showing peritoneal thickening from metastatic renal pelvis carcinoma patients.Med Oncol. 2018 Aug 16;35(10):128. doi: 10.1007/s12032-018-1181-9. Med Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30116986 Free PMC article.
-
Intraperitoneal anatomy with the aid of pathologic fluid and gas: An imaging pictorial review.J Clin Imaging Sci. 2023 May 19;13:13. doi: 10.25259/JCIS_29_2023. eCollection 2023. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2023. PMID: 37292244 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
