Level of radiographic damage and radiographic progression are determinants of physical function: a longitudinal analysis of the TEMPO trial
- PMID: 18203764
- PMCID: PMC2571961
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.081331
Level of radiographic damage and radiographic progression are determinants of physical function: a longitudinal analysis of the TEMPO trial
Abstract
Background: Many studies have examined the relationship between long-term radiographic damage and physical function. However, it is not known if short-term radiographic progression is also associated with physical function.
Aim: To investigate the longitudinal relationship between physical function and both the level of radiographic damage and the radiographic progression rate in patients with early or advanced active rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: The database for the 2-year Trial of Etanercept and Methotrexate with Radiographic Patient Outcomes (TEMPO) was used for this study. Physical function was measured by the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) score at baseline, 6 months and 1 and 2 years. Radiographs of the hands and feet, taken at the same time points, were scored by the van der Heijde-modified Total Sharp Score (TSS). The HAQ score was modelled using generalised mixed linear modelling by TSS or progression in TSS (interval 0-1 year and 1-2 years) adjusted for age, sex, treatment and disease activity.
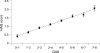
Results: After adjustment for age, sex and disease activity, both TSS and the change in TSS (progression rate) were significant determinants of the HAQ score. When radiographic progression was divided into four categories (negative, zero, minor and greater progression), results showed that HAQ scores tended to be higher with a higher rate of progression. Patients with negative progression scores had lower HAQ scores than patients with positive progression scores.
Conclusions: Patients with greater radiographic damage, and those with recent radiographic progression, have a higher degree of disability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Silman A J, Hochberg M C, eds. Epidemiology of the rheumatic diseases. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 1993
-
- Drossaers-Bakker KW, de Buck M, van Zeben D, Zwinderman AH, Breedveld FC, Hazes JM. Long-term course and outcome of functional capacity in rheumatoid arthritis: the effect of disease activity and radiologic damage over time. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:1854–60 - PubMed
-
- Eberhardt KB, Fex E. Functional impairment and disability in early rheumatoid arthritis—development over 5 years. J Rheumatol 1995;22:1037–42 - PubMed
-
- Pincus T, Sokka T, Wolfe F. Premature mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: evolving concepts [comment]. Arthritis Rheum 2001;44:1234–6 - PubMed
-
- Pincus T, Callahan LF. The ‘side effects’ of rheumatoid arthritis: joint destruction, disability and early mortality. Br J Rheumatol 1993;32(Suppl 1):28–37 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

