PNPase is a key player in the regulation of small RNAs that control the expression of outer membrane proteins
- PMID: 18203924
- PMCID: PMC2248267
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.683308
PNPase is a key player in the regulation of small RNAs that control the expression of outer membrane proteins
Abstract
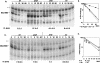
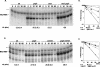
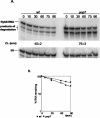
In this report, we demonstrate that exonucleolytic turnover is much more important in the regulation of sRNA levels than was previously recognized. For the first time, PNPase is introduced as a major regulatory feature controlling the levels of the small noncoding RNAs MicA and RybB, which are required for the accurate expression of outer membrane proteins (OMPs). In the absence of PNPase, the pattern of OMPs is changed. In stationary phase, MicA RNA levels are increased in the PNPase mutant, leading to a decrease in the levels of its target ompA mRNA and the respective protein. This growth phase regulation represents a novel pathway of control. We have evaluated other ribonucleases in the control of MicA RNA, and we showed that degradation by PNPase surpasses the effect of endonucleolytic cleavages by RNase E. RybB was also destabilized by PNPase. This work highlights a new role for PNPase in the degradation of small noncoding RNAs and opens the way to evaluate striking similarities between bacteria and eukaryotes.
Figures





References
-
- Amblar, M., Barbas, A., Fialho, A.M., Arraiano, C.M. Characterization of the functional domains of Escherichia coli RNase II. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;360:921–933. - PubMed
-
- Andrade, J.M., Cairrão, F., Arraiano, C.M. RNase R affects gene expression in stationary phase: Regulation of ompA. Mol. Microbiol. 2006;60:219–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
