Clarification and confirmation of the Knack maneuver: the effect of volitional pelvic floor muscle contraction to preempt expected stress incontinence
- PMID: 18204797
- PMCID: PMC2757097
- DOI: 10.1007/s00192-007-0525-3
Clarification and confirmation of the Knack maneuver: the effect of volitional pelvic floor muscle contraction to preempt expected stress incontinence
Abstract
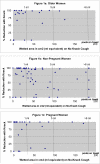
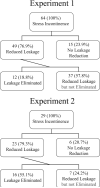
The aim of the study was to determine the immediate effect of timing a pelvic muscle contraction with the moment of expected leakage (the Knack maneuver) to preempt cough-related stress incontinence. Women performed a standing stress test using three hard coughs without and then with the Knack maneuver. Volume of urine loss under both conditions was quantified with paper-towel test. Two groups of women were tested: nonpregnant women (n = 64) and pregnant women (n = 29). In nonpregnant women, wetted area decreased from a median (range) of 43.2 (0.2-183.7) cm2 without the Knack maneuver to 6.9 (range of 0 to 183.7 cm2) with it (p < 0.0001); while in pregnant women it decreased from 14.8 (0-169.7) cm2 to 0 (0-96.5) cm2, respectively (p = 0.001). This study confirms the effect from the Knack maneuver as immediate and provides a partial explanation for early response to widely applied pelvic muscle training regimens in women with stress incontinence.
Figures

References
-
- Miller JM, Ashton-Miller JA, DeLancey JO. A pelvic muscle precontraction can reduce cough-related urine loss in selected women with mild SUI. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1998;46:870–874. - PubMed
-
- Cammu H, Van Nylen M, Derde MP, DeBruyne R, Amy JJ. Pelvic physiotherapy in genuine stress incontinence. Urology. 1991;38(4):332–337. - PubMed
-
- Hay-Smith EJC, Dumoulin C. Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(1) Art. No.:CD005654. DOI 10.1002/14651858.CD005654. - PubMed
-
- Bö K. Pelvic floor muscle training is effective in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, but how does it work? Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunc. 2004;15(2):76–84. - PubMed
-
- Burgio KL, Zyczynski H, Locher JL, Richter HE, Redden DT, Wright KC. Urinary incontinence in the 12-month postpartum period. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102(6):1291–1298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
