Effect of mitogen-activated protein kinases on chemokine synthesis induced by substance P in mouse pancreatic acinar cells
- PMID: 18205703
- PMCID: PMC4401295
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00086.x
Effect of mitogen-activated protein kinases on chemokine synthesis induced by substance P in mouse pancreatic acinar cells
Abstract
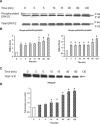
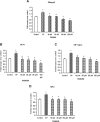
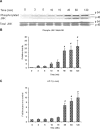
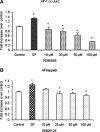
Substance P, acting via its neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1 R), plays an important role in mediating a variety of inflammatory processes. Its interaction with chemokines is known to play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. In pancreatic acinar cells, substance P stimulates the release of NFkappaB-driven chemokines. However, the signal transduction pathways by which substance P-NK1 R interaction induces chemokine production are still unclear. To that end, we went on to examine the participation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in substance P-induced synthesis of pro-inflammatory chemokines, monocyte chemoanractant protein-1 (MCP-I), macrophage inflammatory protein-lalpha (MIP-lalpha) and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2), in pancreatic acini. In this study, we observed a time-dependent activation of ERK1/2, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), NFkappaB and activator protein-1 (AP-1) when pancreatic acini were stimulated with substance P. Moreover, substance P-induced ERK 1/2, JNK, NFkappaB and AP-1 activation as well as chemokine synthesis were blocked by pre-treatment with either extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) inhibitor or JNK inhibitor. In addition, substance P-induced activation of ERK 112, JNK, NFkappaB and AP-1-driven chemokine production were attenuated by CP96345, a selective NK1 R antagonist, in pancreatic acinar cells. Taken together, these results suggest that substance P-NK1 R induced chemokine production depends on the activation of MAPKs-mediated NFkappaB and AP-1 signalling pathways in mouse pancreatic acini.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Role of PKC-delta on substance P-induced chemokine synthesis in pancreatic acinar cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Mar;294(3):C683-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00360.2007. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18160487
-
Role of calcium in substance P-induced chemokine synthesis in mouse pancreatic acinar cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Jul;154(6):1339-48. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.188. Epub 2008 May 19. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18493246 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of SRC family kinases in substance P-induced chemokine production in mouse pancreatic acinar cells and its significance in acute pancreatitis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 May;329(2):418-28. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.148684. Epub 2009 Feb 11. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19211920 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, through nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1, contribute to caerulein-induced expression of substance P and neurokinin-1 receptors in pancreatic acinar cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Mar;332(3):940-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.160416. Epub 2009 Dec 9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20007404
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling and ERK1/2 bistability in asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2011 Feb;41(2):149-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03658.x. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011. PMID: 21121982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular emetic signaling cascades by which the selective neurokinin type 1 receptor (NK1R) agonist GR73632 evokes vomiting in the least shrew (Cryptotis parva).Neurochem Int. 2019 Jan;122:106-119. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.11.012. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Neurochem Int. 2019. PMID: 30453005 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Hydrogen Sulfide, Substance P and Adhesion Molecules in Acute Pancreatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 9;22(22):12136. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212136. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ziziphus nummularia Attenuates the Malignant Phenotype of Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells: Role of ROS.Molecules. 2021 Jul 15;26(14):4295. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144295. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299570 Free PMC article.
-
Role of substance P in the regulation of glucose metabolism via insulin signaling-associated pathways.Endocrinology. 2011 Dec;152(12):4571-80. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1170. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 22009727 Free PMC article.
-
The novel cytokine interleukin-33 activates acinar cell proinflammatory pathways and induces acute pancreatic inflammation in mice.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056866. Epub 2013 Feb 13. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23418608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thurgston G, Baluk P, Hirata A, McDonald DM. Permeability-related changes revealed at endothelial cell borders in inflamed venules by lectin binding. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:H2547–62. - PubMed
-
- Sjodin L, Gylfe E. A selective and potent antagonist of substance P receptors on pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem Int. 1992;27:145–53. - PubMed
-
- Jensen RT, Jones SW, Lu YA, Xu JC, Folkers K, Gardner JD. Interaction of substance P antagonists with substance P receptors on dispersed pancreatic acini. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;804:181–91. - PubMed
-
- Patto RJ, Vinayek R, Jensen RT, Gardner JD. Carbachol does not down-regulate substance P receptors in pancreatic acini. Pancreas. 1992;7:447–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

