Heterogeneity of lymphoid tissue inducer cell populations present in embryonic and adult mouse lymphoid tissues
- PMID: 18205791
- PMCID: PMC2566621
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02750.x
Heterogeneity of lymphoid tissue inducer cell populations present in embryonic and adult mouse lymphoid tissues
Abstract
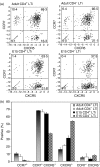
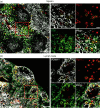
Lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi) cells have a well established role in secondary lymphoid tissue development. Here, we report on the heterogeneity of LTi cells based on their CD4 and chemokine receptor expression. The CD4(-) LTi-cell population has a similar phenotype to the CD4(+) population, with similar chemokine-receptor-expressing subsets. In both embryonic and adult spleen the CD4(-) LTi-cell population is comparable as a proportion of total splenocytes to its CD4(+) counterpart. In contrast, different proportions of CD4(+) and CD4(-) LTi cells are found in different lymph nodes. Both CD4(+) and CD4(-) LTi cells share the anatomical location and are associated with vascular cell adhesion molecule-1-positive stromal cells in spleen and lymph nodes. The numbers of both CD4(+) and CD4(-) LTi cells in adult spleen are augmented in the presence of B cells. With the exception of CD4, there is a strong correlation coefficient (0.89) for gene expression between the two populations. Polymerase chain reaction analysis of individual CD4(+) and CD4(-) LTi cells shows that a similar proportion in embryonic and adult spleen co-expressed both CXCR5 and CCR7 or CXCR5 alone: 84.6% for adult CD4(+) and 87.6% for adult CD4(-); 95.3% for embryonic CD4(+) and 91.5% for embryonic CD4(-). Consistently fewer CCR7 single-positive cells were found in the CD4(+) and CD4(-) fractions in the embryo.
Figures




References
-
- Mebius RE. Organogenesis of lymphoid tissues. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:292–303. - PubMed
-
- Cupedo T, Mebius RE. Cellular interactions in lymph node development. J Immunol. 2005;174:21–5. - PubMed
-
- Kim MY, Gaspal FM, Wiggett HE, et al. CD4(+)CD3(−) accessory cells costimulate primed CD4 T cells through OX40 and CD30 at sites where T cells collaborate with B cells. Immunity. 2003;18:643–54. - PubMed
-
- Kim MY, McConnell FM, Gaspal FM, et al. Function of CD4 + CD3− cells in relation to B- and T-zone stroma in spleen. Blood. 2007;109:1602–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

