GABA receptor activation in the lumbosacral spinal cord decreases detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injured rats
- PMID: 18206170
- PMCID: PMC2744108
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.10.030
GABA receptor activation in the lumbosacral spinal cord decreases detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injured rats
Abstract
Purpose: We investigated the effects of intrathecal application of gamma-aminobutyric acid A and B receptor agonists on detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injured rats.
Materials and methods: Adult female Sprague-Dawley rats were used. At 4 weeks after Th9-10 spinal cord transection awake cystometry and recordings of external urethral sphincter electromyogram were performed to examine the effect of intrathecal application of the gamma-aminobutyric acid A and B agonists muscimol and baclofen or the gamma-aminobutyric acid A and B antagonists bicuculline and saclofen (Tocris Cookson, Ellisville, Missouri), respectively, at the level of the L6-S1 spinal cord. The expression of glutamate decarboxylase 67 mRNA in the L6-S1 spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia was also assessed.
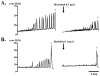
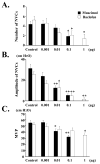
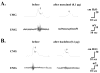
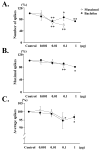
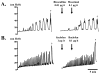
Results: Muscimol and baclofen produced a dose dependent inhibition of the number (51% to 73% decrease) and amplitude (35% to 93% decrease) of nonvoiding bladder contractions and a decrease in micturition pressure. The effects of muscimol and baclofen were antagonized by bicuculline and saclofen, respectively. Bursting activity of external urethral sphincter electromyogram was inhibited, corresponding to the inhibition of bladder activity by muscimol and baclofen. Glutamate decarboxylase 67 mRNA levels in the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia were decreased after spinal cord transection (55% and 84%, respectively).
Conclusions: These results indicate that gamma-aminobutyric acid A and B receptor activation in the spinal cord inhibits detrusor overactivity. The decrease in glutamate decarboxylase 67 mRNA suggests hypofunction of GABAergic inhibitory mechanisms in the spinal cord. Therefore, stimulation of spinal GABAergic mechanisms could be effective for the treatment of detrusor overactivity after spinal cord injury.
Figures
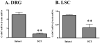
Similar articles
-
Suppression of detrusor-sphincter dysynergia by GABA-receptor activation in the lumbosacral spinal cord in spinal cord-injured rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008 Jul;295(1):R336-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.90315.2008. Epub 2008 May 21. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18495826 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia by herpes simplex virus vector mediated gene delivery of glutamic acid decarboxylase in spinal cord injured rats.J Urol. 2010 Sep;184(3):1204-10. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.04.066. Epub 2010 Jul 21. J Urol. 2010. PMID: 20663524 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus vector-mediated gene delivery of glutamic acid decarboxylase reduces detrusor overactivity in spinal cord-injured rats.Gene Ther. 2009 May;16(5):660-8. doi: 10.1038/gt.2009.5. Epub 2009 Feb 19. Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 19225548 Free PMC article.
-
Urodynamic effects of intravenous and intrathecal administration of E-series prostaglandin 1 receptor antagonist on detrusor overactivity in rats with spinal cord injury.Neurourol Urodyn. 2018 Jan;37(1):132-137. doi: 10.1002/nau.23319. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018. PMID: 28608967
-
The effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor drugs on morphine-induced spastic paraparesis after a noninjurious interval of spinal cord ischemia in rats.Anesth Analg. 2002 Nov;95(5):1389-95, table of contents. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200211000-00053. Anesth Analg. 2002. PMID: 12401631
Cited by
-
Plasticity in reflex pathways to the lower urinary tract following spinal cord injury.Exp Neurol. 2012 May;235(1):123-32. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 May 9. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 21596038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADX71441, a novel, potent and selective positive allosteric modulator of the GABA(B) receptor, shows efficacy in rodent models of overactive bladder.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;171(4):995-1006. doi: 10.1111/bph.12517. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24224799 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in afferent activity after spinal cord injury.Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29(1):63-76. doi: 10.1002/nau.20761. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010. PMID: 20025033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifunctional and multi-system influence of Ghrelin in the treatment of diabetic and spinal cord injury induced Neuropathy.Ann Neurosci. 2011 Jul;18(3):118-22. doi: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.1118309. Ann Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 25205937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of sensory neuron-specific receptor agonist on bladder function in a rat model of cystitis induced by cyclophosphamide.Int Urol Nephrol. 2014 Oct;46(10):1953-9. doi: 10.1007/s11255-014-0734-x. Epub 2014 May 14. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24824147
References
-
- Holstege G, Griffiths D, de Wall H, Dalm E. Anatomical and physiological observations on supraspinal control of bladder and urethral sphincter muscles in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1986;250:449. - PubMed
-
- de Groat WC, Yoshimura N. Mechanisms underlying the recovery of lower urinary tract function following spinal cord injury. Prog Brain Res. 2006;152:59. - PubMed
-
- Miyazato M, Sugaya K, Nishijima S, Ashitomi K, Hatano T, Ogawa Y. Inhibitory effect of intrathecal glycine on the micturition reflex in normal and spinal cord injury rats. Exp Neurol. 2003;183:232. - PubMed
-
- Herman RM, Wainberg MC, delGiudice PF, Willscher MK. The effect of a low dose of intrathecal morphine on impaired micturition reflexes in human subjects with spinal cord lesions. Anesthesiology. 1988;69:313. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro S. Neurotransmission by neurons that use serotonin, noradrenaline, glutamate, glycine, and γ-aminobutyric acid in the normal and injured spinal cord. Neurosurgery. 1997;40:168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

