Endothelial progenitor cells for cardiovascular regeneration
- PMID: 18206807
- PMCID: PMC2276734
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2007.11.004
Endothelial progenitor cells for cardiovascular regeneration
Abstract
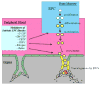
Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are peripheral blood mononuclear cells that can differentiate into mature endothelial cells. Adult EPCs were first discovered in human peripheral blood in 1997. Since then, the potency of EPCs for cardiovascular regeneration has been demonstrated in several preclinical studies; and investigators are beginning to evaluate the therapeutic utility of EPCs in early-phase clinical trials. This review summarizes the progression of basic, preclinical, and clinical research into the potential use of EPC therapy for cardiovascular regeneration.
Figures
References
-
- Asahara T, Masuda H, Takahashi T, et al. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization. Circ Res. 1999a;85:221–228. - PubMed
-
- Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275:964–967. - PubMed
-
- Assmus B, Schachinger V, Teupe C, et al. Transplantation of progenitor cells and regeneration enhancement in acute myocardial infarction (TOPCARE-AMI) Circulation. 2002;106:3009–3017. - PubMed
-
- Bartunek J, Vanderheyden M, Vandekerckhove B, et al. Intracoronary injection of CD133-positive enriched bone marrow progenitor cells promotes cardiac recovery after recent myocardial infarction: feasibility and safety. Circulation. 2005;112:I178–I183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

