Electrophoretic separations on microfluidic chips
- PMID: 18207148
- PMCID: PMC7094303
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.11.119
Electrophoretic separations on microfluidic chips
Abstract
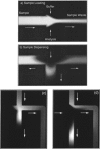
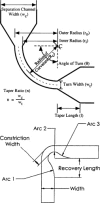
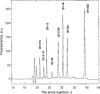
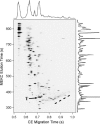
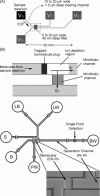
This review presents a brief outline and novel developments of electrophoretic separation in microfluidic chips. Distinct characteristics of microchip electrophoresis (MCE) are discussed first, in which sample injection plug, joule heat, channel turn, surface adsorption and modification are introduced, and some successful strategies and recognized conclusions are also included. Important achievements of microfluidic electrophoresis separation in small molecules, DNA and protein are then summarized. This review is aimed at researchers, who are interested in MCE and want to adopt MCE as a functional unit in their integrated microsystems.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surface modification of the channels of poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic chips with polyacrylamide for fast electrophoretic separations of proteins.Anal Chem. 2004 Apr 1;76(7):2055-61. doi: 10.1021/ac035254s. Anal Chem. 2004. PMID: 15053671
-
Multilayer poly(vinyl alcohol)-adsorbed coating on poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic chips for biopolymer separation.Electrophoresis. 2005 Jan;26(1):211-8. doi: 10.1002/elps.200406157. Electrophoresis. 2005. PMID: 15624173
-
Electrokinetic-driven microfluidic system in poly(dimethylsiloxane) for mass spectrometry detection integrating sample injection, capillary electrophoresis, and electrospray emitter on-chip.Electrophoresis. 2005 Dec;26(24):4674-83. doi: 10.1002/elps.200500338. Electrophoresis. 2005. PMID: 16273585
-
[Research progress on analysis of human papillomavirus by microchip capillary electrophoresis].Se Pu. 2020 Oct 8;38(10):1179-1188. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.05016. Se Pu. 2020. PMID: 34213114 Review. Chinese.
-
Permanent surface modification of polymeric capillary electrophoresis microchips for protein and peptide analysis.Electrophoresis. 2006 Sep;27(18):3533-46. doi: 10.1002/elps.200600082. Electrophoresis. 2006. PMID: 16927422 Review.
Cited by
-
Addressing the global challenges of COVID-19 and other pulmonary diseases with microfluidic technology.Engineering (Beijing). 2022 Jan 27. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2022.01.003. Online ahead of print. Engineering (Beijing). 2022. PMID: 35103108 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing Joule heating in microfluidic thermal gel electrophoresis to create reversible barriers for cell enrichment.Electrophoresis. 2021 Jun;42(11):1238-1246. doi: 10.1002/elps.202000379. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Electrophoresis. 2021. PMID: 33570796 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Surface Treatments of PDMS Microfluidic Devices for Improving Small-Molecule Recovery with Application to Monitoring Metabolites Secreted from Islets of Langerhans.ACS Meas Sci Au. 2023 Aug 24;3(5):380-389. doi: 10.1021/acsmeasuresciau.3c00025. eCollection 2023 Oct 18. ACS Meas Sci Au. 2023. PMID: 37868359 Free PMC article.
-
A review of microdialysis coupled to microchip electrophoresis for monitoring biological events.J Chromatogr A. 2015 Feb 20;1382:48-64. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.12.086. Epub 2015 Jan 10. J Chromatogr A. 2015. PMID: 25637011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Isolation and Enrichment of Nanoparticles.ACS Nano. 2020 Dec 22;14(12):16220-16240. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c06336. Epub 2020 Nov 30. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 33252215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Whitesides G.M. Nature. 2006;442:368. - PubMed
-
- Harrison D.J., Manz A., Fan Z.H., Ludi H., Widmer H.M. Anal. Chem. 1992;64:1926.
-
- Unger M.A., Chou H.P., Thorsen T., Scherer A., Quake S.R. Science. 2000;288:113. - PubMed
-
- Grover W.H., Skelley A.M., Liu C.N., Lagally E.T., Mathies R.A. Sens. Actuators, B. 2003;89:315.
-
- Ng J.M.K., Gitlin I., Stroock A.D., Whitesides G.M. Electrophoresis. 2002;23:3461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

