Cyclooxygenase-2 deficiency enhances Th2 immune responses and impairs neutrophil recruitment in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 18209082
- PMCID: PMC3589995
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.3.1843
Cyclooxygenase-2 deficiency enhances Th2 immune responses and impairs neutrophil recruitment in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
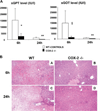
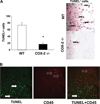
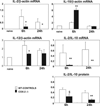
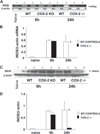
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is a prostanoid-synthesizing enzyme that is critically implicated in a variety of pathophysiological processes. Using a COX-2-deficient mouse model, we present data that suggest that COX-2 has an active role in liver ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. We demonstrate that COX-2-deficient mice had a significant reduction in liver damage after I/R insult. The inability of COX-2(-/-) to elaborate COX-2 products favored a Th2-type response in these mice. COX-2(-/-) livers after I/R injury showed significantly decreased levels of IL-2, as well as IL-12, a cytokine known to have a central role in Th1 effector cell differentiation. Moreover, such livers expressed enhanced levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, shifting the balance in favor of a Th2 response in COX-2-deficient mice. The lack of COX-2 expression resulted in decreased levels of CXCL2, a neutrophil-activating chemokine, reduced infiltration of MMP-9-positive neutrophils, and impaired late macrophage activation in livers after I/R injury. Additionally, Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L) were normally expressed in COX-2(-/-) livers after injury, whereas respective wild-type controls were almost depleted of these two inhibitors of cell death. In contrast, caspase-3 activation and TUNEL-positive cells were depressed in COX-2(-/-) livers. Therefore, our data support the concept that COX-2 is involved in the pathogenic events occurring in liver I/R injury. The data also suggest that potential valuable therapeutic approaches in liver I/R injury may result from further studies aimed at identifying specific COX-2-derived prostanoid pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Howard TK, Klintmalm GB, Cofer JB, Husberg BS, Goldstein RM, Gonwa TA. The influence of preservation injury on rejection in the hepatic transplant recipient. Transplantation. 1990;49:103–107. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H, Farhood A, Smith CW. Neutrophils contribute to ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat liver in vivo. FASEB J. 1990;4:3355–3359. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell-Kenkel JC, Currin RT, Tanaka Y, Thurman RG, Lemasters JJ. Kupffer cell activation and endothelial cell damage after storage of rat livers: effects of reperfusion. Hepatology. 1991;13:83–95. - PubMed
-
- Funk CD. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science. 2001;294:1871–1875. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama C, Tanabe T. Cloning of human gene encoding prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase and primary structure of the enzyme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989;165:888–894. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

