Drosophila neuroblast asymmetric divisions: cell cycle regulators, asymmetric protein localization, and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 18209103
- PMCID: PMC2213578
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200708159
Drosophila neuroblast asymmetric divisions: cell cycle regulators, asymmetric protein localization, and tumorigenesis
Abstract
Over the past decade, many of the key components of the genetic machinery that regulate the asymmetric division of Drosophila melanogaster neural progenitors, neuroblasts, have been identified and their functions elucidated. Studies over the past two years have shown that many of these identified components act to regulate the self-renewal versus differentiation decision and appear to function as tumor suppressors during larval nervous system development. In this paper, we highlight the growing number of molecules that are normally considered to be key regulators of cell cycle events/progression that have recently been shown to impinge on the neuroblast asymmetric division machinery to control asymmetric protein localization and/or the decision to self-renew or differentiate.
Figures
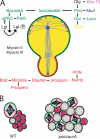
Comment in
-
Cell biology of stem cells: an enigma of asymmetry and self-renewal.J Cell Biol. 2008 Jan 28;180(2):257-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200712159. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18227277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almeida, M.S., and S.J. Bray. 2005. Regulation of post-embryonic neuroblasts by Drosophila Grainyhead. Mech. Dev. 122:1282–1293. - PubMed
-
- Ando, K., T. Ozaki, H. Yamamoto, K. Furuya, M. Hosoda, S. Hayashi, M. Fukuzawa, and A. Nakagawara. 2004. Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) inhibits p53 function by physical interaction and phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 279:25549–25561. - PubMed
-
- Audibert, A., F. Simon, and M. Gho. 2005. Cell cycle diversity involves differential regulation of Cyclin E activity in the Drosophila bristle cell lineage. Development. 132:2287–2297. - PubMed
-
- Beaucher, M., E. Hersperger, A. Page-McCaw, and A. Shearn. 2007. Metastatic ability of Drosophila tumors depends on MMP activity. Dev. Biol. 303:625–634. - PubMed
-
- Bello, B., H. Reichert, and F. Hirth. 2006. The brain tumor gene negatively regulates neural progenitor cell proliferation in the larval central brain of Drosophila. Development. 133:2639–2648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

