Predictors of adherence to antiretroviral therapy in rural Zambia
- PMID: 18209678
- PMCID: PMC2743102
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318165dc25
Predictors of adherence to antiretroviral therapy in rural Zambia
Abstract
Background/objective: Antiretroviral therapy (ART) adherence levels of >or=95% optimize outcomes and minimize HIV drug resistance. As such, identifying barriers to adherence is essential. We sought to assess travel to point-of-care for ART as a potential barrier to adherence in rural Zambia, within the context of patient demographics, perceived stigma, and selected clinical indices.
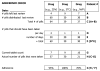
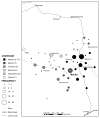
Methods: We studied 424 patients receiving ART from the Macha Mission Hospital (MMH). Interviews ascertained age, gender, education, perceived stigma, nearest rural health facility (RHF), and mode/cost/time of transport for each study participant. Motorcycle odometer and global positioning system way-points measured distance from the MMH to each of the RHFs, estimating patients' home-to-MMH travel distances. Body mass index, World Health Organization HIV/AIDS stage, and pill counts were assessed from review of patients' medical and pharmacy records.
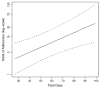
Results: At least 95% adherence was documented for 83.7% of the patients in their first months of ART. Travel-related factors did not predict adherence. Adherence was higher for those on ART for a longer time (odds ratio = 1.04 per day; P = 0.002).
Conclusions: Patients in rural Zambia can achieve adherence rates compatible with good clinical outcomes despite long travel distances. The MMH was able to provide quality HIV/AIDS care by implementing programmatic features selecting for a highly adherent population in this resource-limited setting.
Figures
References
-
- World Bank. World development indicators: Zambia data profile. [Accessed January 27, 2007]. Available at: http://devdata.worldbank.org.proxy.library.vanderbilt.edu/external/CPPro....
-
- Murphy EL, Collier AC, Kalish LA, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy decreases mortality and morbidity in patients with advanced HIV disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

