Role of GSK3 beta in behavioral abnormalities induced by serotonin deficiency
- PMID: 18212115
- PMCID: PMC2234138
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0711496105
Role of GSK3 beta in behavioral abnormalities induced by serotonin deficiency
Abstract
Dysregulation of brain serotonin (5-HT) neurotransmission is thought to underlie mental conditions as diverse as depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, autism, and schizophrenia. Despite treatment of these conditions with serotonergic drugs, the molecular mechanisms by which 5-HT is involved in the regulation of aberrant emotional behaviors are poorly understood. Here, we generated knockin mice expressing a mutant form of the brain 5-HT synthesis enzyme, tryptophan hydroxylase 2 (Tph2). This mutant is equivalent to a rare human variant (R441H) identified in few individuals with unipolar major depression. Expression of mutant Tph2 in mice results in markedly reduced ( approximately 80%) brain 5-HT production and leads to behavioral abnormalities in tests assessing 5-HT-mediated emotional states. This reduction in brain 5-HT levels is accompanied by activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta), a signaling molecule modulated by many psychiatric therapeutic agents. Importantly, inactivation of GSK3beta in Tph2 knockin mice, using pharmacological or genetic approaches, alleviates the aberrant behaviors produced by 5-HT deficiency. These findings establish a critical role of Tph2 in the maintenance of brain serotonin homeostasis and identify GSK3beta signaling as an important pathway through which brain 5-HT deficiency induces abnormal behaviors. Targeting GSK3beta and related signaling events may afford therapeutic advantages for the management of certain 5-HT-related psychiatric conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

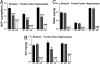
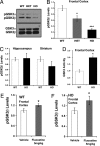

Comment in
-
Role of GSK3beta in behavioral abnormalities induced by serotonin deficiency.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 May 20;105(20):E23; author reply E24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801168105. Epub 2008 May 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18474867 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bonasera SJ, Tecott LH. Mouse models of serotonin receptor function: toward a genetic dissection of serotonin systems. Pharmacol Ther. 2000;88:133–142. - PubMed
-
- Gingrich JA, Hen R. Dissecting the role of the serotonin system in neuropsychiatric disorders using knockout mice. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 2001;155:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Barnes NM, Sharp T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:1083–1152. - PubMed
-
- Berton O, Nestler EJ. New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: beyond monoamines. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:137–151. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu JM. Not only lithium: regulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by antipsychotics and serotonergic drugs. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007;10:3–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

