Generation of shRNAs from randomized oligonucleotides
- PMID: 18213360
- PMCID: PMC2211575
- DOI: 10.1251/bpo129
Generation of shRNAs from randomized oligonucleotides
Abstract
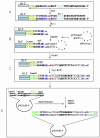
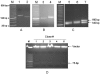
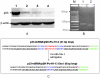
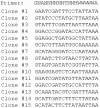
Suppression of gene expression by small interfering RNA (siRNA) has proved to be a gene-specific and cost effective alternative to other gene suppression technologies. Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) generated from the vector-based expression are believed to be processed into functional siRNAs in vivo, leading to gene silencing. Since an shRNA library carries a large pool of potential siRNAs, such a library makes it possible to knock down gene expression at the genome wide scale. Although much of research has been focused on generating shRNA libraries from either individually made gene specific sequences or cDNA libraries, there is no report on constructing randomized shRNA libraries, which could provide a good alternative to these existing libraries. We have developed a method of constructing shRNAs from randomized oligonucleotides. Through this method, one can generate a partially or fully randomized shRNA library for various functional analyses. We validated this procedure by constructing a p53-specific shRNA. Western blot revealed that the p53-shRNA successfully suppressed expression of the endogenous p53 in MCF-7 cells. We then made a partially randomized shRNA library. Sequencing of 15 randomly picked cloned confirmed the randomness of the library. Therefore, the library can be used for various functional assays, such as target validation when a suitable screening or selection method is available.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PCR-based generation of shRNA libraries from cDNAs.BMC Biotechnol. 2006 Jun 21;6:28. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-6-28. BMC Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16790063 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic construction of shRNA library from oligonucleotide library.Genes Genomics. 2019 May;41(5):573-581. doi: 10.1007/s13258-019-00800-2. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Genes Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30830681
-
Construction of simple and efficient DNA vector-based short hairpin RNA expression systems for specific gene silencing in mammalian cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;408:223-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-547-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 18314586
-
RNA-interference-based functional genomics in mammalian cells: reverse genetics coming of age.Oncogene. 2004 Nov 1;23(51):8401-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208176. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15517022 Review.
-
RNA interference: from gene silencing to gene-specific therapeutics.Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Aug;107(2):222-39. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.03.004. Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15908010 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of GAS1 as an epirubicin resistance-related gene in human gastric cancer cells with a partially randomized small interfering RNA library.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 25;284(39):26273-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.028068. Epub 2009 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19638344 Free PMC article.
-
shRNA target prediction informed by comprehensive enquiry (SPICE): a supporting system for high-throughput screening of shRNA library.EURASIP J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2016 Feb 19;2016(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13637-016-0039-8. eCollection 2016 Dec. EURASIP J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2016. PMID: 26941783 Free PMC article.
-
RNA modulators of complex phenotypes in mammalian cells.PLoS One. 2009;4(3):e4758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004758. Epub 2009 Mar 9. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19270743 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

