Pathogenesis of thrombotic microangiopathies
- PMID: 18215115
- PMCID: PMC2582586
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.154311
Pathogenesis of thrombotic microangiopathies
Abstract
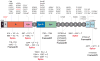
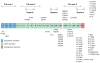
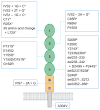
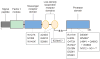
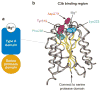
Profound thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia characterize thrombotic microangiopathy, which includes two major disorders: thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS). TTP has at least three types: congenital or familial, idiopathic, and nonidiopathic. The congenital and idiopathic TTP syndromes are caused primarily by deficiency of ADAMTS13, owing to mutations in the ADAMTS13 gene or autoantibodies that inhibit ADAMTS13 activity. HUS is similar to TTP, but is associated with acute renal failure. Diarrhea-associated HUS accounts for more than 90% of cases and is usually caused by infection with Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli (O157:H7). Diarrhea-negative HUS is associated with complement dysregulation in up to 50% of cases, caused by mutations in complement factor H, membrane cofactor protein, factor I or factor B, or by autoantibodies against factor H. The incomplete penetrance of mutations in either ADAMTS13 or complement regulatory genes suggests that precipitating events or triggers may be required to cause thrombotic microangiopathy in many patients.
Figures


References
-
- Moschcowitz E. Hyaline thrombosis of the terminal arterioles and capillaries: a hitherto undescribed disease. Proc NY Pathol Soc. 1924;24:21–24.
-
- Amorosi EL, Ultmann JE. Thrombocytopic purpura: report of 16 cases and review of the literature. Medicine. 1966;45:139–59.
-
- George JN, Gilcher RO, Smith JW, Chandler L, Duvall D, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome: diagnosis and management. J Clin Apher. 1998;13:120–25. - PubMed
-
- George JN. How I treat patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood. 2000;96:1223–29. - PubMed
-
- Bell WR, Braine HG, Ness PM, Kickler TS. Improved survival in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clinical experience in 108 patients. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:398–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

